1
GATE CSE 1995
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The sequence $$.........$$ is an optimal non-preemptive scheduling sequence for the following jobs which leaves the $$CPU$$ idle for $$..........$$ Unit (s) of time


2
GATE CSE 1993
Subjective
+2
-0
The details of an interrupt cycle are shown in Figure
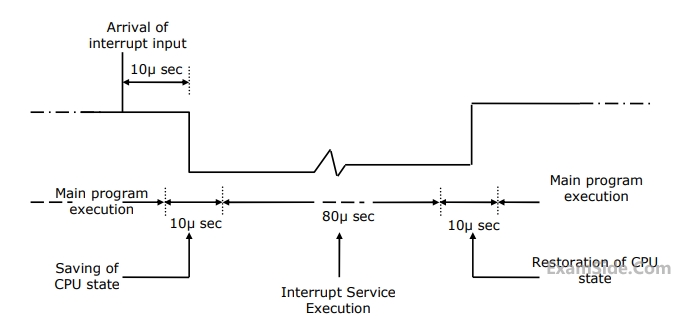
Given that an interrupt input arrives every $$1$$ $$msec,$$ what is the percentage of the total time that the $$CPU$$ devotes for the main program execution.

Given that an interrupt input arrives every $$1$$ $$msec,$$ what is the percentage of the total time that the $$CPU$$ devotes for the main program execution.
3
GATE CSE 1993
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Assume that the following jobs are to be executed on a single processor system.
| Job Id | CPU Burst Time |
|---|---|
| p | 4 |
| q | 1 |
| r | 8 |
| s | 1 |
| t | 2 |
The jobs are assumed to have arrived at time $${0^ + }$$ and in the order $$p,q,r,s,t.$$ Calculate the departure time (completion time) for job $$p$$ if scheduling is round robin with time slice$$1.$$
4
GATE CSE 1992
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Which of the following is an example of a spooled device?
Questions Asked from Process Concepts and Cpu Scheduling (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE CSE 2025 Set 1 (1)
GATE CSE 2024 Set 2 (1)
GATE CSE 2022 (1)
GATE CSE 2020 (1)
GATE CSE 2019 (1)
GATE CSE 2016 Set 2 (1)
GATE CSE 2015 Set 3 (1)
GATE CSE 2015 Set 1 (1)
GATE CSE 2014 Set 3 (1)
GATE CSE 2014 Set 1 (1)
GATE CSE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE CSE 2012 (1)
GATE CSE 2011 (1)
GATE CSE 2009 (1)
GATE CSE 2008 (2)
GATE CSE 2007 (1)
GATE CSE 2006 (2)
GATE CSE 2005 (1)
GATE CSE 2004 (1)
GATE CSE 2003 (1)
GATE CSE 2002 (2)
GATE CSE 2001 (1)
GATE CSE 1999 (2)
GATE CSE 1998 (1)
GATE CSE 1996 (1)
GATE CSE 1995 (1)
GATE CSE 1993 (2)
GATE CSE 1992 (1)
GATE CSE 1990 (1)
GATE CSE 1988 (1)
GATE CSE Subjects
Theory of Computation
Operating Systems
Algorithms
Database Management System
Data Structures
Computer Networks
Software Engineering
Compiler Design
Web Technologies
General Aptitude
Discrete Mathematics
Programming Languages