Synchronization and Concurrency · Operating Systems · GATE CSE
Marks 1
Which of the following statements about threads is/are TRUE?
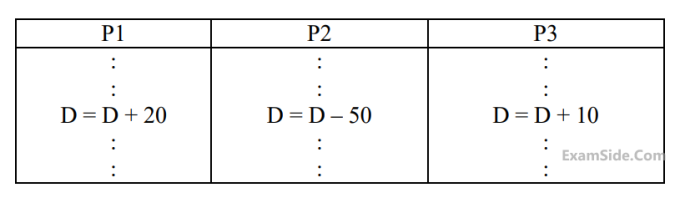
P1( ) {
C = B – 1;
B = 2 * C;
}
P2( ) {
D = 2 * B;
B = D - 1;
}
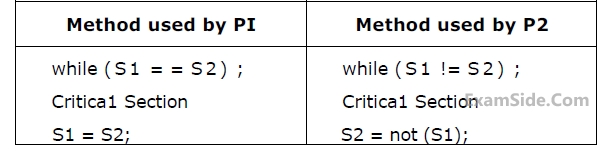
Which of the following statement describes the properties achieved?
wait (m[i]); wait (m(m[(i+1) mod 4]))0;
.......
release (m[i]); release (m[(i+1) mod 4]);
This could cause
Marks 2
Consider the following two threads T1 and T2 that update two shared variables a and b. Assume that initially $a = 1$ and $b = 1$. Though context switching between threads can happen at any time, each statement of T1 or T2 is executed atomically without interruption.
T1:
$a = a + 1$;
$b = b + 1$;
T2:
$b = 2 * b$;
$a = 2 * a$;
Which one of the following options lists all the possible combinations of values of a and b after both T1 and T2 finish execution?
Consider the following code snippet using the fork() and wait() system calls. Assume that the code compiles and runs correctly, and that the system calls run successfully without any errors.
int x = 3;
while(x > 0) {
fork();
printf("hello");
wait(NULL);
x--;
}The total number of times the printf statement is executed is _______
Consider the two functions incr and decr shown below.
incr() {
wait(s);
X = X+1;
signal(s);
}
decr() {
wait(s);
X = X-1;
signal(s);
}
There are 5 threads each invoking incr once, and 3 threads each invoking decr once, on the same shared variable X. The initial value of X is 10.
Suppose there are two implementations of the semaphore s, as follows:
I-1: s is a binary semaphore initialized to 1.
I-2: s is a counting semaphore initialized to 2.
Let V1, V2 be the values of X at the end of execution of all the threads with implementations I-1, I-2, respectively.
Which one of the following choices corresponds to the minimum possible values of V1, V2, respectively?
Consider a computer system with multiple shared resource types, with one instance per resource type. Each instance can be owned by only one process at a time. Owning and freeing of resources are done by holding a global lock (L). The following scheme is used to own a resource instance:
function OWNRESOURCES(Resource R)
Acquire lock L / / a global lock
if R is available then
Acquire R
Release lock L
else
if R is owned by another process P then
Terminate P, after releasing all resources owned by P
Acquire R
Restart P
Release lock L
end if
end if
end function
Which of the following choice(s) about the above scheme is/are correct?
Consider the following multi-threaded code segment (in a mix of C and pseudocode), invoked by two processes P1 and P2, and each of the processes spawns two threads T1 and T2:
int x = 0; // global
Lock L1; // global
main() {
create a thread to execute foo(); // Thread T1
create a thread to execute foo(); // Thread T2
wait for the two threads to finish execution;
print (x);}
foo() {
int y = 0;
Acquire L1;
x = x + 1;
y = y + 1;
Release L1;
print (y); }
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ?

What does the code achieve?
Process X:
private i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
a [i] = f (i);
Exit X (R, S);
}
Process Y:
private i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
Entry Y (R, S);
b [i] = g (a [i] );
}AcquireLock(L){
While (Fetch_And_Add(L,1))
L = 1;
}
Release Lock(L){
L = 0;
}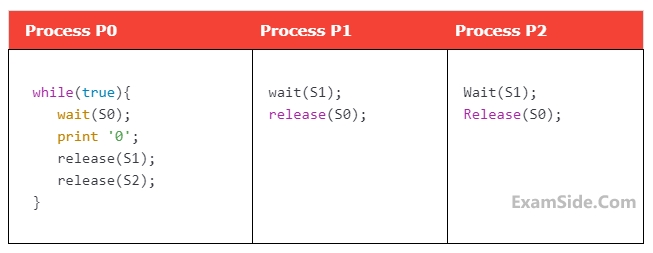 How many times will process P0 print '0'?
How many times will process P0 print '0'?
void enter_CS(X) {
while test-and-set(X) ;
}
void leave_CS(X) {
X=0;
}I. The above solution to CS problem is deadlock-free
II. The solution is starvation free.
III. The processes enter CS in FIFO order.
IV More than one process can enter CS at the same time.
Which of the above statements is TRUE?
P(s): s = s-1;
if s < 0 then wait;
V(s) : s = s-1;
ifs <= 0 then wakeup a process waiting on s;
P(s): Pb (Xb);
S = s - 1;
if(s < 0){
Vb(Xb);
Pb(Yb);
}
Else Vb (Xb);
V(s): Pb (Xb);
S = s + 1;
if(s <= 0) Vb(Yb);
Vb(Xb);
/* P1 */
while(true){
want s1=true;
while(wants2 == true){
/* Critical Section */
wants1 = false;
}
/* Reminder Section */
}
/* P2 */
while(true){
want s2=true;
while(wants1 == true){
/* Critical Section */
Wants2 = false;
}
/* Reminder Section */
}
void barrier (void) {
1: P(S);
2: process_arrived++;
3: V(S);
4: while (process_arrived !=3);
5: P(S);
6: process_left++;
7: if (process_left==3) {
8: process_arrived = 0;
9: process_left = 0;
10: }
11: V(S);
}
The above implementation of barrier is incorrect. Which one of the following is true?
void barrier (void) {
1: P(S);
2: process_arrived++;
3: V(S);
4: while (process_arrived !=3);
5: P(S);
6: process_left++;
7: if (process_left==3) {
8: process_arrived = 0;
9: process_left = 0;
10: }
11: V(S);
}
Which one of the following rectifies the problem in the implementation?
void P (binary_semaphore *s) {
unsigned y;
unsigned *x = &(s->value);
do {
fetch-and-set x, y;
} while (y);
}
void V (binary_semaphore *s) {
S->value = 0;
} Process P:
while(1){
W:
Print '0';
Print '0';
X:
}
Process Q:
while(1){
Y:
Print '1';
Print '1';
Z:
}
Which of the following will ensure that the output string never contains a substring of the form 01n0 or 10n1 where n is odd?
Process P:
while(1){
W:
Print '0';
Print '0';
X:
}
Process Q:
while(1){
Y:
Print '1';
Print '1';
Z:
}
Which of the following will always lead to an output starting with 001100110011
Repeat
flag[i]=true;
turn=j;
while (P) do no-op;
Enter critical section, perform actions, then
exit critical section
Flag[i]=false;
Perform other non-critical section actions.
Until false;
Repeat
P(mutex){
critical section
}
V(mutex)
Forever
N = 2
M = 2
fork L3
fork L4
S1
L1 : join N
S3
L2: join M
S5
L3:S2
goto L1
L4:S4
goto L2
next: