Trees · Data Structures · GATE CSE
Marks 1
Consider a binary tree $T$ in which every node has either zero or two children. Let $n>0$ be the number of nodes in $T$. Which ONE of the following is the number of nodes in $T$ that have exactly two children?
Suppose the values $10,-4,15,30,20,5,60,19$ are inserted in that order into an initially empty binary search tree. Let $T$ be the resulting binary search tree. The number of edges in the path from the node containing 19 to the root node of $T$ is ________ (Answer in integer)
Consider the following $B^{+}$tree with 5 nodes, in which a node can store at most 3 key values. The value 23 is now inserted in the $B^{+}$tree. Which of the following options(s) is/are CORRECT?

Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE for any binary search tree (BST) having $n$ distinct integers?
The height of any rooted tree is defined as the maximum number of edges in the path from the root node to any leaf node.
Suppose a Min-Heap $T$ stores 32 keys. The height of $T$ is ________ (Answer in integer)
Which one of the following sequences when stored in an array at locations $$A[1],....,A[10]$$ forms a max-heap?
Suppose a binary search tree with 1000 distinct elements is also a complete binary tree. The tree is stored using the array representation of binary heap trees. Assuming that the array indices start with 0, the 3rd largest element of the tree is stored at index ___________.
Consider a complete binary tree with 7 nodes. Let A denote the set of first 3 elements obtained by performing Breadth-First Search (BFS) starting from the root. Let B denote the set of first 3 elements obtained by performing Depth-First Search (DFS) starting from the root.
The value of |A - B| is _______
Consider the following statements.
S1 : The sequence of procedure calls corresponds to a preorder traversal of the activation tree.
S2 : The sequence of procedure returns corresponds to a postorder traversal of the activation tree.
Which one of the following options is correct?
Let $T$ be a binary search tree with 15 nodes. The minimum and maximum possible heights of $T$ are :
Note : The height of a tree with a single node is 0.
I. 3, 5, 7, 8, 15, 19, 25
II. 5, 8, 9, 12, 10, 15, 25
III. 2, 7, 10, 8, 14, 16, 20
IV. 4, 6, 7, 9 18, 20, 25
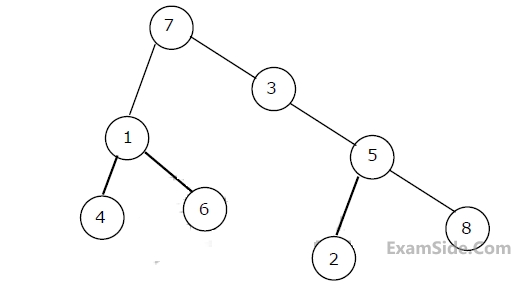
 The order in which the nodes are visited during an in-order traversal of the tree is
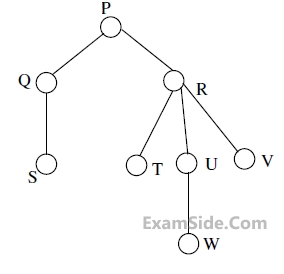
The order in which the nodes are visited during an in-order traversal of the tree is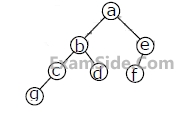
Marks 2
A meld operation on two instances of a data structure combines them into one single instance of the same data structure. Consider the following data structures:
P: Unsorted doubly linked list with pointers to the head node and tail node of the list.
Q: Min-heap implemented using an array.
R: Binary Search Tree.
Which ONE of the following options gives the worst-case time complexities for meld operation on instances of size $n$ of these data structures?
You are given a set $V$ of distinct integers. A binary search tree $T$ is created by inserting all elements of $V$ one by one, starting with an empty tree. The tree $T$ follows the convention that, at each node, all values stored in the left subtree of the node are smaller than the value stored at the node. You are not aware of the sequence in which these values were inserted into $T$, and you do not have access to $T$.
Which one of the following statements is TRUE?
Consider a binary min-heap containing 105 distinct elements. Let k be the index (in the underlying array) of the maximum element stored in the heap. The number of possible values of k is
Let A be a priority queue for maintaining a set of elements. Suppose A is implemented using a max-heap data structure. The operation EXTRACT-MAX(A) extracts and deletes the maximum element from A. The operation INSERT(A, key) inserts a new element key in A. The properties of a max-heap are preserved at the end of each of these operations.
When A contains n elements, which one of the following statements about the worst case running time of these two operations is TRUE?
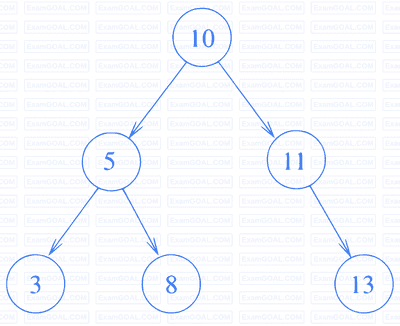
Consider the C function foo and the binary tree shown.
typedef struct node {
int val;
struct node *left, *right;
} node;
int foo(node *p) {
int retval;
if (p == NULL)
return 0;
else {
retval = p->val + foo(p->left) + foo(p->right);
printf("%d ", retval);
return retval;
}
}When foo is called with a pointer to the root node of the given binary tree, what will it print?
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \bullet \,\,\,\,\,$$ Visit the root;
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \bullet \,\,\,\,\,$$ Visit the right subtree using $$New-order;$$
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\, \bullet \,\,\,\,\,$$ Visit the left subtree using $$New-order;$$
The New-order traversal of the expression tree corresponding to the reverse polish expression 3 4 * 5 - 2 ^ 6 7 * 1 + - is given by:
$$Note:\,\,\,The\,\,height\,\,of\,\,a\,tree\,\,with\,\,a\,\,\sin gle\,\,node\,\,is\,\,0$$
int ProcessArray(int *listA, int x, int n)
{
int i, j, k;
i = 0;
j = n-1;
do
{
k = (i+j)/2;
if (x <= listA[k])
j = k-1;
if (listA[k] <= x)
i = k+1;
}
while (i <= j);
if (listA[k] == x)
return(k);
else
return -1;
}typedef struct treeNode* treeptr;
Struct treeNode
{
Treeptr leftMostchild, rightSibiling;
};
Int Dosomething (treeptr tree)
{
int value =0;
if (tree ! = NULL) {
If (tree -> leftMostchild = = NULL)
value=1;
else
value = Dosomething (tree->leftMostchild);
value = value + Dosometing (tree->rightsibiling);
}
return (value);
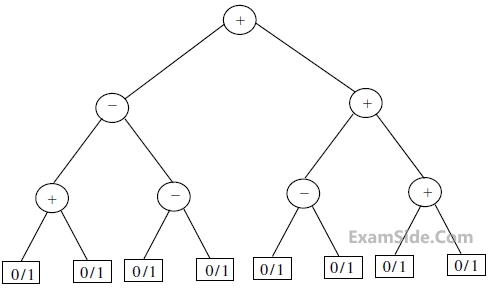
}
int height (treeptr n)
{ if (n== NULL) return -1;
if (n-> left == NULL)
if (n-> right ==NULL) return 0;
else return B1 ; // Box 1
else {h1 = height (n -> left);
if (n -> right == NULL) return (1 + h1);
else {h2 = height (n -> right);
return B2 ; // Box 2
}
}
}I. 81, 537, 102, 439, 285, 376, 305
II. 52, 97, 121, 195, 242, 381, 472
III. 142, 248, 520, 386, 345, 270, 307
IV. 550, 149, 507, 395, 463, 402, 270
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
I. 81, 537, 102, 439, 285, 376, 305
II. 52, 97, 121, 195, 242, 381, 472
III. 142, 248, 520, 386, 345, 270, 307
IV. 550, 149, 507, 395, 463, 402, 270
Suppose the BST has been unsuccessfully searched for key 273. Which all of the above sequences list nodes in the order in which we could have encountered them in the search?
struct CellNode
{
struct CellNOde *leftChild;
int element;
struct CellNode *rightChild;
};
int GetValue(struct CellNode *ptr)
{
int value = 0;
if (ptr != NULL)
{
if ((ptr->leftChild == NULL) &&
(ptr->rightChild == NULL))
value = 1;
else
value = value + GetValue(ptr->leftChild)
+ GetValue(ptr->rightChild);
}
return(value);
} i) preorder and postorder
ii) inorder and postorder
iii) preorder and inorder
iv) level order and postorder
struct CellNode{
struct CellNode *leftChild;
int element;
struct CellNode *rightChild;
};
int Dosomething (struct CellNode *ptr) {
int value = 0;
if (ptr ! = NULL)
{ if (ptr - > leftChild ! = NULL)
value = 1 + DoSomething (ptr - > leftChild);
if (ptr - > rightChild ! = NULL)
value = max(value,1 + DoSomething (ptr - > rightChild));
}
return (value);
}