Network Layer · Computer Networks · GATE CSE
Marks 1
A machine receives an IPv4 datagram. The protocol field of the IPv4 header has the protocol number of a protocol X .
Which ONE of the following is NOT a possible candidate for X ?
Consider a network that uses Ethernet and IPv4. Assume that IPv4 headers do not use any options field. Each Ethernet frame can carry a maximum of 1500 bytes in its data field. A UDP segment is transmitted. The payload (data) in the UDP segment is 7488 bytes. Which ONE of the following choices has the CORRECT total number of fragments transmitted and the size of the last fragment including IPv4 header?
Node X has a TCP connection open to node Y. The packets from X to Y go through an intermediate IP router R. Ethernet switch S is the first switch on the network path between X and R. Consider a packet sent from X to Y over this connection.
Which of the following statements is/are TRUE about the destination IP and MAC addresses on this packet at the time it leaves X?
Which of the following statements about IPv4 fragmentation is/are TRUE?
Which of the following fields of an IP header is/are always modified by any router before it forwards the IP packet?
Which of the following fields is/are modified in the IP header of a packet going out of a network address translation (NAT) device from an internal network to an external network?
Consider an enterprise network with two Ethernet segments, a web server and a firewall, connected via three routers as shown below.

What is the number of subnets inside the enterprise network?
Consider the following two statements.
S1 : Destination MAC address of an ARP reply is a broadcast address.
S2 : Destination MAC address of an ARP request is a broadcast address.
Which one of the following choices is correct?
I. A router does not modify the IP packets during forwarding.
II. It is not necessary for a router to implement any routing protocol.
III. A router should reassemble IP fragments if the MTU of the outgoing link is larger than the size of the incoming IP packet.
Which of the above statements is/are TRUE?
(i) TTL
(ii) Checksum
(iii) Fragment Offset
Marks 2
Suppose a message of size 15000 bytes is transmitted from a source to a destination using IPv4 protocol via two routers as shown in the figure. Each router has a defined maximum transmission unit (MTU) as shown in the figure, including IP header. The number of fragments that will be delivered to the destination is _________ . (Answer in integer)

Which one of the following CIDR prefixes exactly represents the range of IP addresses 10.12.2.0 to 10.12.3.255?
Consider a network path P—Q—R between nodes P and R via router Q. Node P sends a file of size $10^6$ bytes to R via this path by splitting the file into chunks of $10^3$ bytes each. Node P sends these chunks one after the other without any wait time between the successive chunk transmissions. Assume that the size of extra headers added to these chunks is negligible, and that the chunk size is less than the MTU.
Each of the links P—Q and Q—R has a bandwidth of $10^6$ bits/sec, and negligible propagation latency. Router Q immediately transmits every packet it receives from P to R, with negligible processing and queueing delays. Router Q can simultaneously receive on link P—Q and transmit on link Q—R.
Assume P starts transmitting the chunks at time $t = 0$.
Which one of the following options gives the time (in seconds, rounded off to 3 decimal places) at which R receives all the chunks of the file?
Consider the entries shown below in the forwarding table of an IP router. Each entry consists of an IP prefix and the corresponding next hop router for packets whose destination IP address matches the prefix. The notation “/N” in a prefix indicates a subnet mask with the most significant N bits set to 1.
| Prefix | Next hop router |
|---|---|
| 10.1.1.0/24 | R1 |
| 10.1.1.128/25 | R2 |
| 10.1.1.64/26 | R3 |
| 10.1.1.192/26 | R4 |
This router forwards 20 packets each to 5 hosts. The IP addresses of the hosts are 10.1.1.16, 10.1.1.72, 10.1.1.132, 10.1.1.191, and 10.1.1.205 . The number of packets forwarded via the next hop router R2 is _______
Consider sending an IP datagram of size 1420 bytes (including 20 bytes of IP header) from a sender to a receiver over a path of two links with a router between them. The first link (sender to router) has an MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) size of 542 bytes, while the second link (router to receiver) has an MTU size of 360 bytes.
The number of fragments that would be delivered at the receiver is ______________
Consider a computer network using the distance vector routing algorithm in its network layer. The partial topology of the network is as shown below.

The objective is to find the shortest-cost path from the router R to routers P and Q. Assume that R does not initially know the shortest routes to P and Q. Assume that R has three neighbouring routers denoted as X, Y, and Z. During one iteration, R measures its distance to its neighbours X, Y, and Z as 3, 2, and 5, respectively. Router R gets routing vectors from its neighbours that indicate that the distance to router P from routers X, Y, and Z are 7, 6, and 5, respectively. The routing vector also indicates that the distance to router Q from routers X, Y, and Z are 4, 6, and 8, respectively. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct with respect to the new routing table of R, after updation during this iteration ?
I. 202.61.84.0/21
II. 202.61.104.0/21
III. 202.61.64.0/21
IV. 202.61.144.0/21
Consider three machines M, N, and P with IP addresses 100.10.5.2, 100.10.5.5, and 100.10.5.6 respectively. The subnet mask is set to 255.255 .255 .252 for all the three machines. Which one of the following is true?
Suppose that in an IP-over-Ethernet network, a machine X wishes to find the MAC address of another machine Y in its subnet. Which one of the following techniques can be used for this?
The number of fragments that the IP datagram will be divided into for transmission is ________.

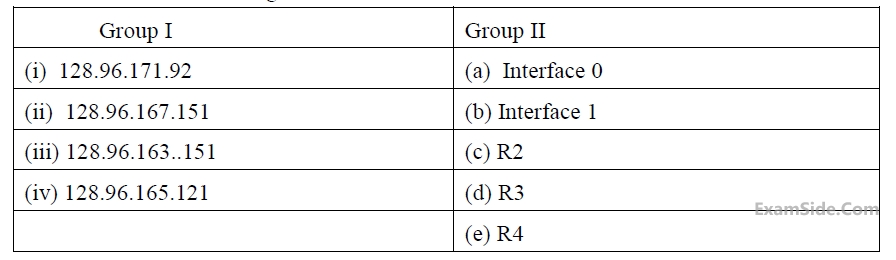
For each IP address in Group I identify the correct choice of the next hop from Group II using the entries from the routing table above.

The identifier of the output interface on which this packet will be forwarded is ______.
Q—R1—R2—R3—H
H acts as an HTTP server, and Q connects to H via HTTP and downloads a file. Session layer encryption is used, with DES as the shared key encryption protocol. Consider the following four pieces of information:
$$[I1]$$ The URL of the file downloaded by Q
$$[I2]$$ The TCP port numbers at Q and H
$$[I3]$$ The IP addresses of Q and H
$$[I4]$$ The link layer addresses of Q and H
The ISP wants to give half of this chunk of addresses to Organization A, and a quarter to Organization B, while retaining the remaining with itself. Which of the following is a valid allocation of address to A and B?
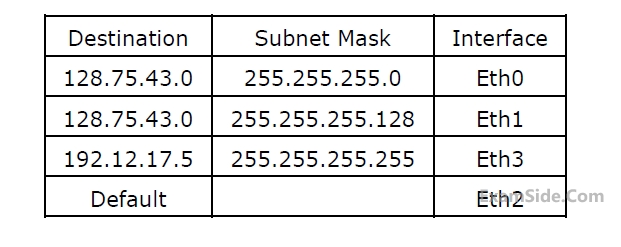
On which interface will the router forward packets addressed to destinations 128.75.43.16 and 192.12.17.10 respectively?