Memory Interfacing · Computer Organization · GATE CSE
Marks 1
Let WB and WT be two set associative cache organizations that use LRU algorithm for cache block replacement. WB is a write back cache and WT is a write through cache. Which of the following statements is/are FALSE?
Consider a computer system with a byte-addressable primary memory of size 232 bytes. Assume the computer system has a direct-mapped cache of size 32 KB (1 KB = 210 bytes), and each cache block is of size 64 bytes.
The size of the tag field is ______ bits.
Marks 2
For a direct-mapped cache, 4 bits are used for the tag field and 12 bits are used to index into a cache block. The size of each cache block is one byte. Assume that there is no other information stored for each cache block. Which ONE of the following is the CORRECT option for the sizes of the main memory and the cache memory in this system (byte addressable), respectively?
Given a computing system with two levels of cache (L1 and L2) and a main memory. The first level (L1) cache access time is 1 nanosecond (ns) and the "hit rate" for L1 cache is $90 \%$ while the processor is accessing the data from L1 cache. Whereas, for the second level (L2) cache, the "hit rate" is $80 \%$ and the "miss penalty" for transferring data from L2 cache to L1 cache is 10 ns . The "miss penalty" for the data to be transferred from main memory to L2 cache is 100 ns . Then the average memory access time in this system in nanoseconds is (rounded off to one decimal place)
Consider a memory system with 1 M bytes of main memory and 16 K bytes of cache memory. Assume that the processor generates 20-bit memory address, and the cache block size is 16 bytes. If the cache uses direct mapping, how many bits will be required to store all the tag values?
[Assume memory is byte addressable, $1 \mathrm{~K}=2^{10}$, $1 \mathrm{M}=2^{20}$]
A computer has a memory hierarchy consisting of two-level cache (L1 and L2) and a main memory. If the processor needs to access data from memory, it first looks into L1 cache. If the data is not found in L1 cache, it goes to L2 cache. If it fails to get the data from L2 cache, it goes to main memory, where the data is definitely available. Hit rates and access times of various memory units are shown in the figure. The average memory access time in nanoseconds (ns) is _________ . (Rounded off to two decimal places)

Consider two set-associative cache memory architectures: WBC, which uses the write back policy, and WTC, which uses the write through policy. Both of them use the LRU (Least Recently Used) block replacement policy. The cache memory is connected to the main memory. Which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
A given program has 25% load/store instructions. Suppose the ideal CPI (cycles per instruction) without any memory stalls is 2. The program exhibits 2% miss rate on instruction cache and 8% miss rate on data cache. The miss penalty is 100 cycles. The speedup (rounded off to two decimal places) achieved with a perfect cache (i.e., with NO data or instruction cache misses) is ______
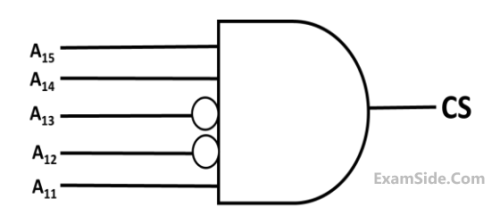
A 4 kilobyte (KB) byte-addressable memory is realized using four 1 KB memory blocks. Two input address lines (IA4 and IA3) are connected to the chip select (CS) port of these memory blocks through a decoder as shown in the figure. The remaining ten input address lines from IA11-IA0 are connected to the address port of these blocks. The chip select (CS) is active high.

The input memory address (IA11-IA0), in decimal, for the starting locations (Addr=0) of each block (indicated as X1, X2, X3, X4 in the figure) are among the options given below. Which one of the following options is CORRECT?
An 8-way set associative cache of size 64 KB (1 KB = 1024 bytes) is used in a system with 32-bit address. The address is sub-divided into TAG, INDEX, and BLOCK OFFSET.
The number of bits in the TAG is __________.
Consider a system with 2 KB direct mapped data cache with a block size of 64 bytes. The system has a physical address space of 64 KB and a word length of 16 bits. During the execution of a program, four data words P, Q, R, and S are accessed in that order 10 times (i.e., PQRSPQRS .....). Hence, there are 40 accesses to data cache altogether. Assume that the data cache is initially empty and no other data words are accessed by the program. The addresses of the first bytes of P, Q, R, and S are 0$$\times$$A248, 0$$\times$$C28A, 0$$\times$$CA8A, and 0$$\times$$A262, respectively. For the execution of the above program, which of the following statements is/are TRUE with respect to the data cache?
Assume a two-level inclusive cache hierarchy, L1 and L2, where L2 is the larger of the two. Consider the following statements.
S1 : Read misses in a write through L1 cache do not result in writebacks of dirty lines to the L2.
S2 : Write allocate policy must be used in conjunction with write through caches and no-write allocate policy is used with writeback caches.
Which of the following statements is correct?
A1 = 0x42C8A4, A2 = 0x546888, A3 = 0x6A289C, A4 = 0x5E4880
Which one of the following is TRUE?

The smallest cache size required to ensure an average read latency of less than $$6$$ $$ms$$ is _________ $$MB.$$
The size of the cache tag directory is
The number of bit in the tag field of an address is
$$\,\,\,\,$$$$1$$ Valid bit
$$\,\,\,\,$$$$1$$ Modified bit
As many bits as the minimum needed to identify the memory block mapped in the cache.
What is the total size of memory needed at the cache controller to store meta-data (tags) for the cache?
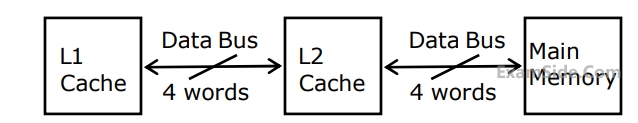
When there is a miss in $$L1$$ cache and a hit in $$L2$$ cache, a block is transferred from $$L2$$ cache to $$L1$$ cache. What is the time taken for this transfer?

When there is a miss in both $$L1$$ cache and $$L2$$ cache, first a block is transferred from main memory to $$L2$$ cache, and then a block is transferred from $$L2$$ cache to $$L1$$ cache.
What is the total time taken for these transfers?
0, 255, 1, 4, 3, 8, 133, 159, 216, 129, 63, 8, 48, 32, 73, 92, 155.
Which one of the following memory block will NOT be in cache if $$LRU$$ replacement policy is used?
$$1.$$ $$L1$$ must be a write-through cache
$$2.$$ $$L2$$ must be a write-through cache
$$3.$$ The associativity of $$L2$$ must be greater than that of $$L1$$
$$4.$$ The $$L2$$ cache must be at least as large as the $$L1$$ cache
How many data cache misses will occur in total?
Which of the following lines of the data cache will be replaced by new blocks in accessing the array?
The value of $${h_1}$$ is
The value of $${h_2}$$ is
(i) How many bits are required for addressing the main memory?
(ii) How many bits are needed to represent the TAG, SET and WORD fields?
Marks 5
(a)$$\,\,\,\,$$ What is the number of sets in the cache?
(b)$$\,\,\,\,$$ What is the size (in bits) of the tag field per cache block?
(c)$$\,\,\,\,$$ What is the number and size of comparators required for tag matching?
(d)$$\,\,\,\,$$ How many address bits are required to find the byte offset within a cache block?
(e)$$\,\,\,\,$$ What is the total amount of extra memory (in bytes) required for the tag bits?

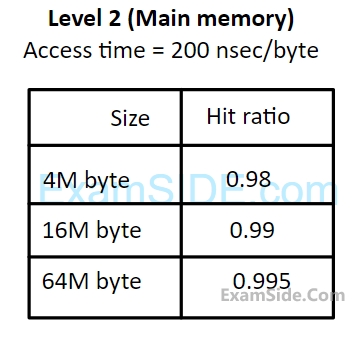

(i) What should be the minimum size of level $$1$$ and $$2$$ memories to achieve an average access time of less than $$100$$ nsec?
(ii) What is the average access time achieved using the chosen sizes of level $$1$$ and level $$2$$ memories?