Structured Query Language · Database Management System · GATE CSE
Marks 1

The primary key of each table is indicated by underlying the constituent fields.
SELECT s.sno, s.sname
FROM Suppliers s, Catalogue c
WHERE s.sno = c.sno AND
Cost > (SELECT AVG (cost)
FROM Catalogue
WHERE pno = ‘P4’
GROUP BY pno);The number of rows returned by the above SQL query is
Book (isbn, bname), Stock (isbn, copies)SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B INNER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B LEFT OUTER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B RIGHT OUTER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;SELECT B.isbn, S.copies
FROM Book B FULL OUTER JOIN Stock S
ON B.isbn = S.isbn;$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Cinema(theater, address, capacity)
Which of the following options will be needed at the end of the $$SQL$$ query
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ SELECT $$P1.$$address
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ FROM Cinema $$P1$$
such that it always finds the addresses of theaters with maximum capacity?
S1: A foreign key declaration can always be replaced by an equivalent check assertion in SQL.
S2: Given the table R(a,b,c) where a and b together form the primary key, the following is a valid table definition.
CREATE TABLE S (
a INTEGER,
d INTEGER,
e INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY (d),
FOREIGN KEY (a) references R)Which one of the following statements is CORRECT?
P: An SQL query can contain a HAVING clause even if it does not have a GROUP BY clause
Q: An SQL query can contain a HAVING clause only if it has a GROUP BY clause
R: All attributes used in the GROUP BY clause must appear in the SELECT clause
S: Not all attributes used in the GROUP BY clause need to appear in the SELECT clause
A relational schema for a train reservation database is given below:
Passenger ( pid, pname, age)
Reservation (pid, cass, tid)
Table: Passenger
| pid | pname | age |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 'Sachin' | 65 |
| 1 | 'Rahul' | 66 |
| 2 | 'Sourav' | 67 |
| 3 | 'Anil' | 69 |
Table: Reservation
| pid | class | tid |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 'AC' | 8200 |
| 1 | 'AC' | 8201 |
| 2 | 'SC' | 8201 |
| 5 | 'AC' | 8203 |
| 1 | 'SC' | 8204 |
| 3 | 'AC' | 8202 |
What pids are returned by the following SQL query for the above instance of the tables?
SELECT pid
FROM Reservation
WHERE class 'AC' AND
EXISTS (SELECT *
FROM Passenger
WHERE age > 65
AND Passenger.pid = Reservation.pid);Students (rollno, name, address)
Enroll(rollno,courseno, coursename)Marks 2
Consider the following relational schema:
Students ($$\mathrm{\underline {rollno:integer}}$$, name: string, age: integer, cgpa: real)
Courses ($$\mathrm{\underline {courseno:integer}}$$, cname: string, credits: integer)
Enrolled ($$\mathrm{\underline {rollno:integer}}$$, $$\mathrm{\underline {courseno:integer}}$$, grade: string)
Which of the following options is/are correct SQL query/queries to retrieve the names of the students enrolled in course number (i.e., courseno) $1470 ?$
Consider the following database tables of a sports league.
player(pid, pname, age)
team(tid, tname, city, cid)
coach(cid, cname)
members(pid, tid)
An instance of the table and an SQL query are given.

The value returned by the given SQL query is ________ . (Answer in integer)
Consider the following table named Student in a relational database. The primary key of this table is rollNum.
Student
| rollNum | name | gender | marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Naman | M | 62 |
| 2 | Aliya | F | 70 |
| 3 | Aliya | F | 80 |
| 4 | James | M | 82 |
| 5 | Swati | F | 65 |
The SQL query below is executed on this database.
SELECT *
FROM Student
WHERE gender = 'F' AND
marks > 65;
The number of rows returned by the query is _____________.
Consider the relational database with the following four schemas and their respective instances.
Student( $$\underline {sNo} $$ , sName, dNo) Dept( $$\underline {dNo} $$ , dName)
Course( $$\underline {cNo} $$ , cName, dNo) Register( $$\underline {sNo} $$ , $$\underline {cNo} $$ )

SQL Query :
SELECT * FROM Student AS S WHERE NOT EXIST
(SELECT cNo FROM Course WHERE dNo = "D01"
EXCEPT
SELECT cNo FROM Register WHERE sNo = S.sNo)
The number of rows returned by the above SQL query is _____________.
The relation scheme given below is used to store information about the employees of a company, where empId is the key and deptId indicates the department to which the employee is assigned. Each employee is assigned to exactly one department.
emp(empId, name, gender, salary, deptId)
Consider the following SQL query:
select deptId, count(⋆)
from emp
where gender = "female" and salary > (select avg(salary) from emp)
group by deptId;
The above query gives, for each department in the company, the number of female employees whose salary is greater than the average salary of
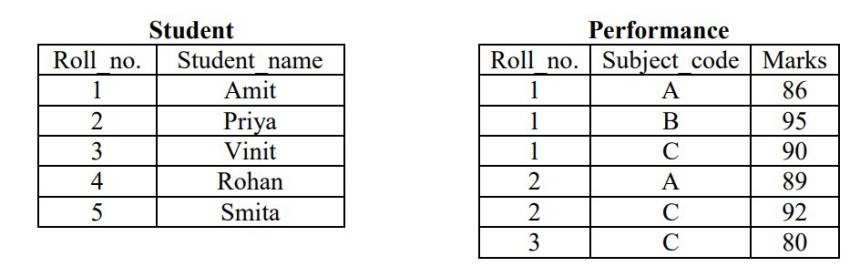
The primary key of the Student table is Roll_no. For the Performance table, the columns Roll_no. and Subject_code together from the primary key. Consider the SQL query given below:
SELECT S.Student_name, sum (P.Marks)
FROM Student S, Performance P
WHERE P.Marks > 84
GROUP BY S.Student_name;The number of rows returned by the above SQL query is _________.
| water_schemes | ||
|---|---|---|
| scheme_no | district_name | capacity |
| 1 | Ajmer | 20 |
| 1 | Bikaner | 10 |
| 2 | Bikaner | 10 |
| 3 | Bikaner | 20 |
| 1 | Churu | 10 |
| 2 | Churu | 20 |
| 1 | Dungargarh | 10 |
The number of tuples returned by the following $$SQL$$ query is _______________.
with total(name, capacity) as
select district_name, sum(capacity)
from water_schemes
group by district_name
with total_avg(capacity) as
select avg(capacity)
from total
select name
from total, total_avg
where total.capacity ≥ total_avg.capacityConsider the following relation:
Student
| Roll_No | Student_Name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Raj |
| 2 | Rohit |
| 3 | Raj |
Performance
| Roll_No | Course | Marks |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Math | 80 |
| 1 | English | 70 |
| 2 | Math | 75 |
| 3 | English | 80 |
| 2 | Physics | 65 |
| 3 | Math | 80 |
Consider the following SQL query.
SELECT S.Student_Name, Sum(P.Marks)
FROM Student S, Performance P
WHERE S.Roll_No= P.Roll_No
GROUP BY S.STUDENT_NameConsider the following relational schema:
employee (empId, empName, empDept )
customer (custId, custName, salesRepId, rating)
SalesRepId is a foreign key referring to empId of the employee relation. Assume that each employee makes a sale to at least one customer. What does the following query return?SELECT empName
FROM employee E
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT custId
FROM customer C
WHERE C.salesRepId = E.empId
AND C.rating <> 'GOOD');Given the following schema:
employees(emp-id, first-name, last-name, hire-date, dept-id, salary)
departments(dept-id, dept-name, manager-id, location-id)
You want to display the last names and hire dates of all latest hires in their respective departments in the location ID 1700. You issue the following query:SQL> SELECT last-name, hire-date
FROM employees WHERE (dept-id, hire-date) IN
(SELECT dept-id, MAX(hire-date)
FROM employees JOIN departments USING(dept-id)
WHERE location-id = 1700
GROUP BY dept-id);Select * from R where a in (select S.a from S)Consider the following relational schema.
Students(rollno: integer, sname: string)
Courses(courseno: integer, cname: string)
Registration(rollno: integer, courseno: integer, percent: real)
Which of the following queries are equivalent to this query in English?"Find the distinct names of all students who score more than 90% in the course numbered 107"
(I) SELECT DISTINCT S.sname
FROM Students as S, Registration as R
WHERE R.rollno=S.rollno AND
R.courseno=107 AND R.percent >90(II) ∏sname(σcourseno = 107 ∧ percent > 90 (Registration ⋈ Students))
(III) { T | ∃S ∈ Students, ∃R ∈ Registration ( S.rollno=R.rollno ∧ R.courseno=107 ∧ R.percent > 90 ∧ T.sname=S.sname)}
(iv) { < SN >| ∃SR∃RP ( < SR, SN > ∈ Students ∧ ∈ Registration ∧ RP > 90)}
Database table by name Loan_Records is given below.
| Borrower | Bank_Manager | Loan_Amount |
|---|---|---|
| Ramesh | Sunderajan | 10000.00 |
| Suresh | Ramgopal | 5000.00 |
| Mahesh | Sunderajan | 7000.00 |
What is the output of the following SQL query?
SELECT count(*)
FROM (
(SELECT Borrower. Bank_Manager FROM Loan_Records) AS S
NATURAL JOIN
(SELECT Bank_Manager, Loan_Amount FROM Loan_Records) AS T );Consider a database table T containing two columns X and Y each of type integer. After the creation of the table, one record (X = 1, Y = 1) is inserted in the table.
Let MX and MY denote the respective maximum values of X and Y among all records in the table at any point in time. Using MX and MY, new records are inserted in the table 128 times with X and Y values being MX + 1, 2*MY + 1 respectively. It may be noted that each time after the insertion, values of MX and MY change.
What will be the output of the following SQL query after the steps mentioned above are carried out?
SELECT Y FROM T WHERE X=7; Suppliers(sid : integer, sname : string, city : string, street : string)
Parts(pid : integer, pname : string, color : string)
Catalog(sid : integer, pid : integer, cost : real)
Consider the following relational query on the above database:SELECT S.sname
FROM Suppliers S
WHERE S.sid NOT IN
(SELECT C.sid
FROM Catalog C
WHERE C.pid NOT IN
(SELECT P.pid
FROM Parts P
WHERE P.color<> 'blue'))Suppliers(sid : integer, sname : string, city : string, street : string)
Parts(pid : integer, pname : string, color : string)
Catalog(sid : integer, pid : integer, cost : real)
Assume that, in the suppliers relation above, each supplier and each street within a city has a unique name, and (sname, city) forms a candidate key. No other functional dependencies are implied other than those implied by primary and candidate keys. Which one of the following is TRUE about the above schema?Consider The Following Relational Scheme
Student (school-id, sch-roll-no, sname, saddress)
School (school-id, sch-name, sch-address, sch-phone)
Enrolment (school-id, sch-roll-no, erollno, examname)
ExamResult (Erollno, examname, marks)
SELECT sch-name, COUNT (*)
FROM School C, Enrolment E,
ExamResult R
WHERE E.school-id = C.school-id
AND E.examname = R.examname
AND E.erollno = R.erollno
AND R.marks = 100 AND S.school-id IN
(SELECT school-id
FROM student
GROUP BY school-id
HAVING COUNT (*) > 200)
GROUP BY school-id;Consider The Following Relational Scheme
Student (school-id, sch-roll-no, sname, saddress)
School (school-id, sch-name, sch-address, sch-phone)
Enrolment (school-id, sch-roll-no, erollno, examname)
ExamResult (Erollno, examname, marks)
Consider the following tuple relational calculus query
{ t | ∃E ∈ Enrolment t = E.school-id ∧
| { x | x ∈ ExamResult B.school-id =
t ∧ ( ∃B ∈ ExamResult B.erollno =
x.erollno ∧ B.examname = x.examname ∧
B.marks > 35 } | ÷ |
{ x | x ∈ Enrolment ∧ x.school-id = t }
| * 100 > 35 }Q1:
Select e.empId
From employee e
Where not exists
(Select * From employee s
where s.department = "5" and
s.salary >=e.salary);Q2:
Select e.empId
From employee e
Where e.salary > Any
( Select distinct salary
From employee s
Where s.department = "5");Query1:
Select A.customer, count(B.customer)
From account A, account B
Where A.balance <=B.balance
Group by A.customer
Query2:
Select A.customer, 1+count(B.customer)
From account A, account B
Where A.balance < B.balance
Group by A.customerConsider these statements about Query1 and Query2.
1. Query1 will produce the same row set as Query2 for some but not all databases.
2. Both Query1 and Query2 are correct implementation of the specification
3. Query1 is a correct implementation of the specification but Query2 is not
4. Neither Query1 nor Query2 is a correct implementation of the specification
5. Assigning rank with a pure relational query takes less time than scanning in decreasing balance order assigning ranks using ODBC.
Which two of the above statements are correct?Consider the relation "enrolled (student, course)" in which (student, course) is the primary key, and the relation "paid (student, amount)" where student is the primary key. Assume no null values and no foreign keys or integrity constraints. Given the following four queries:
Query 1:
Select student
from enrolled
where student in (select student from paid)Query 2:
Select student
from paid
where student in (select student from enrolled)Query 3:
Select E.student
from enrolled E, paid P
where E.student = P.studentQuery 4:
Select student
from paid
where exists (Select *
from enrolled
where enrolled.student = paid.student)Which one of the following statements is correct?
Consider a database with three relation instances shown below. The primary keys for the Drivers and Cars relation are Did and cid respectively and the records are stored in ascending order of these primary keys as given in the tables. No indexing is available in the database.
D: Drivers Relation
| Did | Dname | rating | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | Karthikeyan | 7 | 25 |
| 29 | Salman | 1 | 33 |
| 31 | Boris | 8 | 55 |
| 32 | Amoldt | 8 | 25 |
| 58 | Schumacher | 10 | 35 |
| 64 | Sachin | 7 | 35 |
| 71 | Senna | 10 | 16 |
| 74 | Sachin | 9 | 35 |
| 85 | Rahul | 3 | 25 |
| 95 | Ralph | 3 | 53 |
R: Reserves Relation
| Did | cid | Day |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | 101 | 10/10/06 |
| 22 | 102 | 10/10/06 |
| 22 | 103 | 8/10/06 |
| 22 | 104 | 7/10/06 |
| 31 | 102 | 10/11/06 |
| 31 | 103 | 6/11/06 |
| 31 | 104 | 12/11/06 |
| 64 | 101 | 5/9/06 |
| 64 | 102 | 8/9/06 |
| 74 | 103 | 8/9/06 |
C: Cars relation
| cid | Cname | Color |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Renault |
Blue |
| 102 | Renault |
Red |
| 103 | Ferrari | Green |
| 104 | Jaguar | Red |
Select D.dname
From Drivers D
Where D.did in (SELECT R.did
From Cars C,Reserves R
WHERE R.cid = C.cid and C.color = 'green')Let n be the number of comparisons performed when the above SQL query is optimally executed. If linear search is used to locate a tuple in a relation using primary key, then n lies in the range
Consider a database with three relation instances shown below. The primary keys for the Drivers and Cars relation are Did and cid respectively and the records are stored in ascending order of these primary keys as given in the tables. No indexing is available in the database.
D: Drivers Relation
| Did | Dname | rating | Age |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22 | Karthikeyan | 7 | 25 |
| 29 | Salman | 1 | 33 |
| 31 | Boris | 8 | 55 |
| 32 | Amoldt | 8 | 25 |
| 58 | Schumacher | 10 | 35 |
| 64 | Sachin | 7 | 35 |
| 71 | Senna | 10 | 16 |
| 74 | Sachin | 9 | 35 |
| 85 | Rahul | 3 | 25 |
| 95 | Ralph | 3 | 53 |
R: Reserves Relation
| Did | cid | Day |
|---|---|---|
| 22 | 101 | 10/10/06 |
| 22 | 102 | 10/10/06 |
| 22 | 103 | 8/10/06 |
| 22 | 104 | 7/10/06 |
| 31 | 102 | 10/11/06 |
| 31 | 103 | 6/11/06 |
| 31 | 104 | 12/11/06 |
| 64 | 101 | 5/9/06 |
| 64 | 102 | 8/9/06 |
| 74 | 103 | 8/9/06 |
C: Cars relation
| cid | Cname | Color |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | Renault |
Blue |
| 102 | Renault |
Red |
| 103 | Ferrari | Green |
| 104 | Jaguar | Red |
What is the output of the following SQL query?
Select D.dname
From Drivers D
Where D.did in (SELECT R.did
From Cars C,Reserves R
WHERE R.cid = C.cid and C.color = 'green')A company maintains records of sales made by its salespersons and pays them commission based on each individual’s total sales made in a year. This data is maintained in a table with following schema:
salesinfo = (salespersonid, totalsales, commission)In a certain year, due to better business results, the company decides to further reward its salespersons by enhancing the commission paid to them as per the following formula:
If commission < = 50000, enhance it by 2%
If 50000 < commission < = 100000, enhance it by 4%
If commission > 100000, enhance it by 6%
The IT staff has written three different SQL scripts to calculate enhancement for each slab, each of these scripts is to run as a separate transaction as follows:
T1: Update salesinfo
Set commission = commission * 1.02
Where commission < = 50000;
T2: Update salesinfo
Set commission = commission * 1.04
Where commission > 50000 and commission is < = 100000;
T3: Update salesinfo
Set commission = commission * 1.06
Where commission > 100000;Select title
From book as B
Where (select count(*)
From book as T
Where T.price > B.price) < 5;Supply = (supplierid, itemcode)
Inventory = (itemcode, warehouse, stocklevel)
For a specific information required by the management, following SQL query has been written
Select distinct STMP.supplierid
From Supply as STMP
Where not unique (Select ITMP.supplierid
From Inventory, Supply as ITMP
Where STMP.supplierid = ITMP.supplierid
And ITMP.itemcode = Inventory.itemcode
And Inventory.warehouse = 'Nagpur');Table: Student
| Roll_no | Name | Dept_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ABC | 1 |
| 2 | DEF | 1 |
| 3 | GHI | 2 |
| 4 | JKL | 3 |
Table: Department
| Dept_id | Dept_name |
|---|---|
| 1 | A |
| 2 | B |
| 3 | C |
Roll_no is the primary key of the Student table, Dept_id is the primary key of the
Department table and Studetn.Dept_id is a foreign key from
Department. Dept_id.
(i) update Student set Dept_id = Null where Roll_no =1
(ii) update Department set Dept_id = Null where Dept_id =1 Insert into department values (1, ‘Mathematics’)
Insert into department values (2, ‘Physics’)
Insert into student values (1, ‘Navin’,1)
Insert into student values (2, ‘Mukesh’,2)
Insert into student values (3, ‘Gita’,1)Select * from student, department;The employee information in a company is stored in the relation
Employee (name, sex, salary, deptName)Consider the following SQL query
Select deptName
From Employee
Where sex = ‘M’
Group by deptName
Having avg(salary) >
(Select avg (salary) From Employee);
Students: (Roll_number, Name, Date_of_birth)
Courses: (Course number, Course_name, Instructor)
Grades: (Roll_number, Course_number, Grade)
Select distinct Name
From Students, Courses, Grades
Where Students.Roll_number = Grades.Roll_number
and Courses.Instructor = 'Korth'
and Courses.Course_number = Grades.Course_number
and Grades.grade = 'A';
select distinct w,x
from r, s;EMP (Employee-no, Dept-no, Employee-name, Salary)
DEPT (Dept-no, Dept-name, Location)
Write an SQL query to:
(a) Find all employee names who work in departments located at "Calcutta" and whose salary is greater than Rs.50,000.
(b) Calculate, for each department number, the number of employees with a salary greater than Rs.1,00,000.
Suppose we have a database consisting of the following three relations.
FREQUENTS (student, parlor) giving the parlors each student visits.
SERVES (parlor, ice-cream) indicating what kind of ice-creams each parlor serves.
LIKES (student, ice-cream) indicating what ice-creams each student likes.
(Assume that each student likes at least one ice-cream and frequents at least one parlor)Express the following in SQL:
Print the students that frequent at least one parlor that serves some ice-cream that they like.