Linked List · Data Structures · GATE CSE
Marks 1
Let SLLdel be a function that deletes a node in a singly-linked list given a pointer to the node and a pointer to the head of the list. Similarly, let DLLdel be another function that deletes a node in a doubly-linked list given a pointer to the node and a pointer to the head of the list.
Let $$n$$ denote the number of nodes in each of the linked lists. Which one of the following choices is TRUE about the worst-case time complexity of SLLdel and DLLdel?
Consider the problem of reversing a singly linked list. To take an example, given the linked list below:

the reversed linked list should look like

Which one of the following statements is TRUE about the time complexity of algorithms that solve the above problem in O(1) space?
An algorithm performs the following operations on the list in this order:
$$\Theta \left( N \right),\,\,delete,\,\,O\left( {\log N} \right)\,insert,\,$$ $$\,O\left( {\log N} \right)\,fund, and $$ $$\Theta \left( N \right)\,$$ $$decrease$$-$$key.$$ What is the time complexity of all these operations put together?
Marks 2
Let LIST be a datatype for an implementation of linked list defined as follows:
typedef struct list {
int data;
struct list *next;
} LIST;
Suppose a program has created two linked lists, L1 and L2, whose contents are given in the figure below (code for creating L1 and L2 is not provided here). L1 contains 9 nodes, and L2 contains 7 nodes. Consider the following C program segment that modifies the list L1. The number of nodes that will be there in L1 after the execution of the code segment is _________. (Answer in integer)


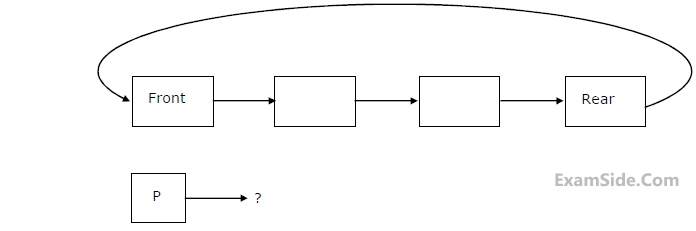
Which one of the following is the time complexity of the most time-efficient implementation of $$enqueue$$ and $$dequeue,$$ respectively, for this data structure?
typedef struct node {
int value;
struct node *next;
} Node;
Node *move_to_front(Node *head) {
Node *p, *q;
if ((head = = NULL: || (head->next = = NULL)) return head;
q = NULL; p = head;
while (p-> next !=NULL) {
q=P;
p=p->next;
}
return head;
} struct node {
int value;
struct node *next;
};
Void rearrange (struct node *list ){
struct node *p, * q;
int temp;
if( !list || !list-> next) return;
p = list; q = list->next;
while (q) {
temp = p->value;
p-> value = q ->value;
q-> value = temp;
p = q-> next;
q = p ? p->next : 0;
}
}struct node {
int value;
struct node *next;
};
Void rearrange (struct node *list ){
struct node *p, * q;
int temp;
if( !list || !list-> next) return;
p = list; q = list->next;
while (q) {
temp = p->value;
p-> value = q ->value;
q-> value = temp;
p = q-> next;
q = p ? p->next : 0;
}
}
struct item {
int data;
struct item * next;
};
int f(struct item *p) {
return ((p == NULL) || (p ->next == NULL) ||
((p->data <= p -> next -> data) &&
f(p-> next)));
}