Hashing · Data Structures · GATE CSE
Marks 1
An algorithm has to store several keys generated by an adversary in a hash table. The adversary is malicious who tries to maximize the number of collisions. Let $$k$$ be the number of keys, $$m$$ be the number of slots in the hash table, and $$k > m$$. Which one of the following is the best hashing strategy to counteract the adversary?
Suppose we are given n keys, m has table slots, and two simple uniform hash functions h1 and h2. Further suppose our hashing scheme uses h1 for the odd keys and h2 for the even keys. What is the expected number of keys in a slot?
h1(k)=k mod 23, and the secondary hash function is h2(k)=1+(k mod 19).
Assume that the table size is 23. Then the address returned by probe 1 in the probe sequence (assume that the probe sequence begins at probe 0) for key value k=90 is _______.
i. A hash function (these are often used for computing digital signatures) is an injective function.
ii. encryption technique such as DES performs a permutation on the elements of its input alphabet.
Which one of the following options is valid for the above two statements?
i) 9679, 1989, 4199 hash to the same value
ii) 1471, 6171 has to the same value
iii) All elements hash to the same value
iv) Each element hashes to a different value
Marks 2
In a double hashing scheme, $h_1(k)=k \bmod 11$ and $h_2(k)=1+(k \bmod 7)$ are the auxiliary hash functions. The size $m$ of the hash table is 11 . The hash function for the $i^{\text {th }}$ probe in the open address table is $\left[h_1(k)+i h_2(k)\right]$ mod $m$. The following keys are inserted in the given order: $63,50,25,79,67,24$.
The slot at which key 24 gets stored is _______. (Answer in integer)
Consider a dynamic hashing approach for 4-bit integer keys:
1. There is a main hash table of size 4.
2. The 2 least significant bits of a key is used to index into the main hash table.
3. Initially, the main hash table entries are empty.
4. Thereafter, when more keys are hashed into it, to resolve collisions, the set of all keys corresponding to a main hash table entry is organized as a binary tree that grows on demand.
5. First, the 3rd least significant bit is used to divide the keys into left and right subtrees.
6. to resolve more collisions, each node of the binary tree is further sub-divided into left and right subtrees based on 4th least significant bit.
7. A split is done only if it is needed, i. e. only when there is a collision.
Consider the following state of the hash table.
 Which of the following sequence of key insertions can cause the above state of the hash table (assume the keys are in decimal notation)?
Which of the following sequence of key insertions can cause the above state of the hash table (assume the keys are in decimal notation)?
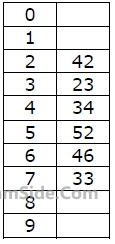 How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?
How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above? Which one of the following choices gives a possible order in which the key values could have been inserted in the table?
Which one of the following choices gives a possible order in which the key values could have been inserted in the table?43 36 92 87 11 4 71 13 14 is inserted into an initially empty hash table, the bins of which are indexed from zero to ten. What is the index of the bin into which the last record is inserted?