1
GATE EE 2001
Subjective
+5
-0
A synchronous generator is connected to an infinite bus through a lossless double circuit transmission line. The generator is delivering 1.0 per unit power at a load angle of $${30^0}$$ when a sudden fault reduces the peak power that can be transmitted to 0.5 per unit. After clearance of fault, the peak power that can be transmitted becomes 1.5 per unit. Find the critical clearing angle.
2
GATE EE 2000
Subjective
+5
-0
A synchronous generator, having a reactance of 0.15 p.u., is connected to an infinite bus through two identical parallel transmission lines having reactance of 0.3 p.u. each. In steady state, the generator is delivering 1 p.u. Power to the infinite bus. For a three phase fault at the receiving end of one line, calculate the rotor angle at the end of first time step of 0.05 seconds. Assume the voltage behind transient reactance for the generator as 1.1 p.u. and infinite bus voltage as 1.0 p.u. Also indicate how the accelerating powers will be evaluated for the next time step if the breaker clears the fault.
(i) at the end of an interval
(ii) at the middle of an interval.
3
GATE EE 1998
Subjective
+5
-0
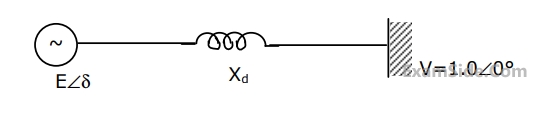
An alternator is connected to an infinite bus as shown in figure. It delivers 1.0 p.u. current at 0.8 p.f lagging at V = 1.0 p.u.. The reactance Xd of the alternator is 1.2 p.u. Determine the active power output and the steady state power limit. Keeping the active power fixed, if the excitation is reduced, find the critical excitation corresponding to operation at stability limit.

4
GATE EE 1997
Subjective
+5
-0
A synchronous motor is receiving 50% of the power it is cable to receiving from an infinite bus. If the load on the motor is suddenly reduced to 80% of the previous value, swing of the motor around is new equilibrium position.
Questions Asked from Power System Stability (Marks 5)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE EE Subjects
Electric Circuits
Electromagnetic Fields
Signals and Systems
Electrical Machines
Engineering Mathematics
General Aptitude
Power System Analysis
Electrical and Electronics Measurement
Analog Electronics
Control Systems
Power Electronics