1
GATE EE 2012
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
L et y[n] denote the convolution of h[n] and g[n], where $$h\left[n\right]=\left(1/2\right)^nu\left[n\right]$$ and g[n] is a causal
sequence. If y[0] = 1 and y[1] = 1/2, then g[1] equals
2
GATE EE 2011
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The response h(t) of a linear time invariant system to an impulse $$\delta\left(t\right)$$, under
initially relaxed condition is $$h\left(t\right)=e^{-t}\;+\;e^{-2t}$$. The response of this system for a
unit step input u(t) is
3
GATE EE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
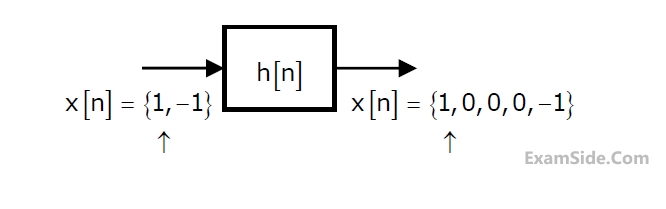
Given the finite length input x[n] and the corresponding finite length output y[n]
of an LTI system as shown below, the impulse response h[n] of the system is

4
GATE EE 2009
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A cascade of 3 Linear Time Invariant systems is casual and unstable. From this, we conclude that
Questions Asked from Linear Time Invariant Systems (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE EE Subjects
Electric Circuits
Electromagnetic Fields
Signals and Systems
Electrical Machines
Engineering Mathematics
General Aptitude
Power System Analysis
Electrical and Electronics Measurement
Analog Electronics
Control Systems
Power Electronics