1
GATE ECE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
A plane wave in free space with
$$\overrightarrow E = \left( {\sqrt \pi } \right)\left( {10.0\,\widehat x + 11.8\,\widehat y} \right)\exp \left[ {j\left( {4\pi \times {{10}^8}\,t - k\,z} \right)} \right]$$
where $$\widehat x$$ and $$\widehat y$$ are unit vectors in the $$x$$- and $$y$$-directions respectively is incident normally on a semi-infinite block of ice as shown in Fig. For ice, $$\mu = {\mu _0},\,\,\,\sigma = 0$$ and $$\varepsilon = 9{\varepsilon _0}\left( {1 - j0.001} \right)$$.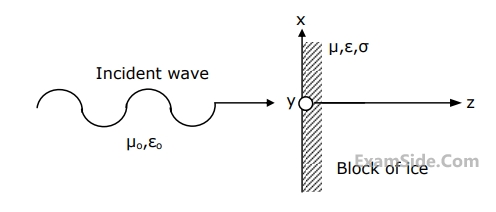
$$\overrightarrow E = \left( {\sqrt \pi } \right)\left( {10.0\,\widehat x + 11.8\,\widehat y} \right)\exp \left[ {j\left( {4\pi \times {{10}^8}\,t - k\,z} \right)} \right]$$
where $$\widehat x$$ and $$\widehat y$$ are unit vectors in the $$x$$- and $$y$$-directions respectively is incident normally on a semi-infinite block of ice as shown in Fig. For ice, $$\mu = {\mu _0},\,\,\,\sigma = 0$$ and $$\varepsilon = 9{\varepsilon _0}\left( {1 - j0.001} \right)$$.
(a) Calculate the average power density associated with the incident wave.
(b) Calculate the skin depth in ice.
(c) Estimate the average power density at a distance of 5 times the skins depth in the ice block, measured from the interface.

2
GATE ECE 1999
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A transmitting antenna radiates 251 W isotropically. A receiving antenna, located 100m away from the transmitting antenna, has an effective aperture of 500 cm2. The total power received by the antenna is
3
GATE ECE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
The average power of an omni-directional antenna varies as the magnitude of cos($$\theta $$) where $$\theta $$ is the azimuthal angle. Calculate the maximum Directive Gain of the antenna and the angles at which it occurs.
4
GATE ECE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
A 100 m section of an air-filled rectangular wave-guide operating in the $$T{E_{10}}$$ mode has a cross-sectional dimension of 1.071 cm $$ \times $$ 0.5 cm. Two pulses carriers of 21 GHz and 28 GHz are simultaneously launched at one end of the wave-guide section. What is the time delay difference between the two pulses at the other end of the waveguide?
Paper analysis
Total Questions
Analog Circuits
8
Communications
4
Control Systems
10
Digital Circuits
10
Electromagnetics
10
Electronic Devices and VLSI
1
Engineering Mathematics
1
Microprocessors
1
Network Theory
8
Signals and Systems
8
More papers of GATE ECE
GATE ECE 2025
GATE ECE 2024
GATE ECE 2023
GATE ECE 2022
GATE ECE 2021
GATE ECE 2019
GATE ECE 2018
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2
GATE ECE 2016 Set 1
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3
GATE ECE 2015 Set 1
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2
GATE ECE 2013
GATE ECE 2012
GATE ECE 2011
GATE ECE 2010
GATE ECE 2009
GATE ECE 2008
GATE ECE 2007
GATE ECE 2006
GATE ECE 2005
GATE ECE 2004
GATE ECE 2003
GATE ECE 2002
GATE ECE 2001
GATE ECE 2000
GATE ECE 1999
GATE ECE 1998
GATE ECE 1997
GATE ECE 1996
GATE ECE 1995
GATE ECE 1994
GATE ECE 1993
GATE ECE 1992
GATE ECE 1991
GATE ECE 1990
GATE ECE 1989
GATE ECE 1988
GATE ECE 1987
GATE ECE
Papers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2019
2018
2014
2013
2012
2011
2010
2009
2008
2007
2006
2005
2004
2003
2002
2001
2000
1999
1998
1997
1996
1995
1994
1993
1992
1991
1990
1989
1988
1987