Consider three IP networks A, B and C. Host HA in networks A sends messages each containing 180 bytes of application data to a host HC in network C. The TCP layer prefixes a 20 byte header to the message. This passes through an intermediate network B. the maximum packet size, including 20 byte IP header, in each network is:
A : 1000 bytesB : 100 bytes
C : 1000 bytes
The network A and B are connected through a 1 Mbps link, while B and C are connected by a 512 Kbps link (bps = bits per second).
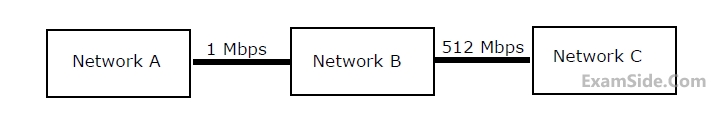
Assuming that the packets are correctly delivered, how many bytes, including headers, are delivered to the IP layer at the destination for one application message, in the best case? Consider only data packets.
Consider three IP networks A, B and C. Host HA in networks A sends messages each containing 180 bytes of application data to a host HC in network C. The TCP layer prefixes a 20 byte header to the message. This passes through an intermediate network B. the maximum packet size, including 20 byte IP header, in each network is:
A : 1000 bytesB : 100 bytes
C : 1000 bytes
The network A and B are connected through a 1 Mbps link, while B and C are connected by a 512 Kbps link (bps = bits per second).
 What is the rate at which application data is transferred to host HC? Ignore errors, acknowledgements, and other overheads.
What is the rate at which application data is transferred to host HC? Ignore errors, acknowledgements, and other overheads.