GATE EE

Two monoshots, one positive edge triggered and other negative edge triggered, are connected as shown in the figure. The pulse widths of the two monoshot options, $${Q_1}$$ and $${Q_2}$$ are $${T_{O{N_1}}}$$ and $${T_{O{N_2}}}$$ respectively.

The frequency and the duty cycle of the signal at $${Q_1}$$ will respectively be


If the voltage $${v_1}$$ is made $$+2.5$$ $$V,$$ the voltage waveform at $$'P'$$ will become.

The output of the filter in above is given to the circuit shown in figure The gain $${V_S}$$ frequency characteristic of the $$0/p$$ $$\left( {{V_0}} \right)$$ will be


If $${R_1} = {R_2} = {R_A}$$ and $${R_3} = {R_4} = {R_B},$$ the circuit acts as a

It is desired to make full wave rectifier using two half wave rectifiers. The resultant circuit will be


(a)

(b)
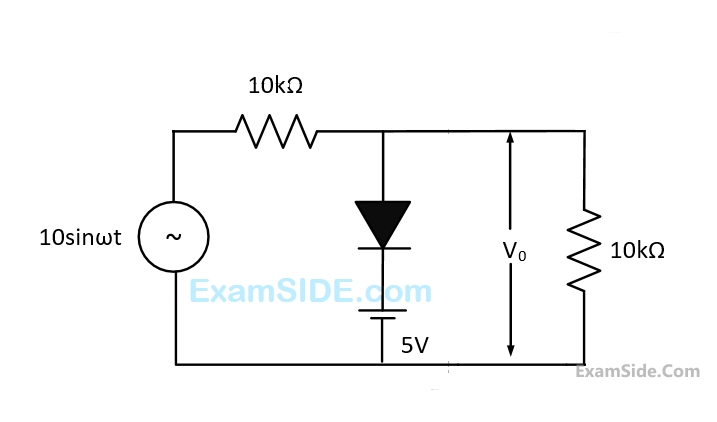
If such diodes are used in the clipper circuit of figure given above, the output voltage (V0) of the circuit will be
The steady state value of the output of the system for a unit impulse input applied at time instant $$t=1$$ will be
A unity feedback is provided to the above system $$G(s)$$ to make it a closed loop system as shown in figure.

For a unit step input $$r(t),$$ the steady state error in the input will be
The transfer function $$G(s)$$ of this system will be
Which one of the following statements is correct?

This transfer function has

The range of $$k$$ for which system is stable will by given by
Where $$\delta \left( t \right)$$ is the delta function. Assuming zero initial condition, and denoting the unit step function by $$u(t),y(t)$$ can be of the form


The contents of stack pointer $$(SP),$$ program counter $$(PC)$$ and $$(HL)$$ are $$270H,$$ $$2100H$$ and $$0000H$$ respectively. When the following sequence of instructions are executed,
$$2100H:$$ $$DAD$$ $$SP$$
$$2101H;$$ $$PCHL$$
The contents of $$(SP)$$ and $$(PC)$$ at the end of execution will be







The excitation voltage and load angle will respectively be
Keeping the excitation voltage same, the load on the motor is increased such that the motor current increases by $$20\% $$. The operating power factor will become

The motor is coupled to a $$220$$ $$V$$, separately excited $$d.c.$$ generator feeding power to fixed resistance of $$10\Omega .$$ Two watt-meter method is used to measure the input power to induction motor. The variable resistance is adjusted such that motor recorded
$${W_1} = 1800\,W,\,\,{W_2} = - 200\,W.$$
Neglecting all losses of both the machines, the $$dc$$ generator power output and the current through resistance $$\left( {{R_{ex}}} \right)$$ will respectively be

The motor is coupled to a $$220$$ $$V$$, separately excited $$d.c.$$ generator feeding power to fixed resistance of $$10\Omega .$$ Two watt-meter method is used to measure the input power to induction motor. The variable resistance is adjusted such that motor recorded
$${W_1} = 1800\,W,\,\,{W_2} = - 200\,W.$$
The Speed of rotation of stator magnetic field with respect to rotor structure will be
$$R = 1.0\,\Omega ,{X_s} = X{'_r} = 1.5\,\Omega $$ Neglect stator resistance and core and rotational losses of the motor. The motor is controlled from a $$3$$-phase voltage source inverter with constant $$V/f$$ control. The stator line-to-line voltage $$(rms)$$ and frequency to obtain the maximum torque at starting will be:


The induced $$emf$$ $$\left( {{e_{rs}}} \right)$$ in the secondary winding as a function of time will be of the form

The transformer connection will be represented by
$${W_1}:250\,\,V,\,\,\,10\,\,A,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Low Power Factor
$${W_2}:250\,\,V,\,\,\,5\,\,A,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Low Power Factor
$${W_3}:150\,\,V,\,\,\,10\,\,A,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ High Power Factor
$${W_4}:150\,\,V,\,\,\,5\,\,A,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ High Power Factor
The watt-meters used in open circuit test and short circuit test of the transformer will respectively be
The net voltage across the armature resistance at the time of plugging will be
The external resistance to be added in the armature circuit to limit the armature current to $$125\% $$ of its rated value is
$$\alpha \left( \lambda \right) = \left| {\lambda {\rm I} - P} \right| = {\lambda ^3} + 2\lambda + {\lambda ^2} + 1 = 0.$$
If $${\rm I}$$ denotes identity matrix then the inverse of $$P$$ will be


Assume that the load inductance is sufficient to ensure continuous and ripple free load current. The firing angle of the bridge for a load current of $${{\rm I}_0} = 10\,\,A$$ will be

If the firing pulses are suddenly removed, the steady state voltage $$\left( {{V_0}} \right)$$ waveform of the converter will become

The inverter is operated at $$50$$ $$Hz$$ in $${180^0}$$ square wave mode. Assume that the load current does not have any $$dc$$ component. The peak value of the inductor current $${i_0}$$ will be

The average voltage across the load and the average current through the diode will respectively be
$${C_1}\left( {{P_{G1}}} \right) = {P_{G1}} + 0.055 \times P_{G1}^2$$
$${C_2}\left( {{P_{G2}}} \right) = 3{P_{G2}} + 0.03 \times P_{G2}^2$$
Where $${P_{G1}}$$ and $${P_{G2}}$$ are the MW injections from generator $${G_1}$$ and $${G_2}$$ respectively. Thus, the minimum cost dispatch will be
Nominal system frequency $$= 50$$ $$Hz.$$ The reference voltage for phase $$'a'$$ is defined as $$\,\,V\left( t \right) = {V_m}\,\cos \left( {\omega t} \right).\,\,\,$$ A symmetrical $$3\phi $$ fault occurs at centre of the line, i.e., at point $$'F'$$ at time 'to' the $$+ve$$ sequence impedance from source $${S_1}$$ to point $$'F'$$ equals $$(0.004 + j \,\,0.04)$$ $$p.u.$$ The wave form corresponding to phase $$'a'$$ fault current from bus $$X$$ reveals that decaying $$d.c.$$ offset current is $$-ve$$ and in magnitude at its maximum initial value. Assume that the negative sequence are equal to $$+ve$$ sequence impedances and the zero sequence $$(Z)$$ are $$3$$ times $$+ve$$ sequence $$(Z).$$
Instead of the three phase fault, if a single line to ground fault occurs on phase $$' a '$$ at point $$' F '$$ with zero fault impedance, then the $$rms$$ of the ac component of fault current $$\left( {{{\rm I}_x}} \right)$$ for phase $$'a'$$ will be
Nominal system frequency $$= 50$$ $$Hz.$$ The reference voltage for phase $$'a'$$ is defined as $$\,\,V\left( t \right) = {V_m}\,\cos \left( {\omega t} \right).\,\,\,$$ A symmetrical $$3\phi $$ fault occurs at centre of the line, i.e., at point $$'F'$$ at time 'to' the $$+ve$$ sequence impedance from source $${S_1}$$ to point $$'F'$$ equals $$(0.004 + j \,\,0.04)$$ $$p.u.$$ The wave form corresponding to phase $$'a'$$ fault current from bus $$X$$ reveals that decaying $$d.c.$$ offset current is $$-ve$$ and in magnitude at its maximum initial value. Assume that the negative sequence are equal to $$+ve$$ sequence impedances and the zero sequence $$(Z)$$ are $$3$$ times $$+ve$$ sequence $$(Z).$$
The instant $$\,\left( {{t_0}} \right)\,\,$$ of the fault will be
Nominal system frequency $$= 50$$ $$Hz.$$ The reference voltage for phase $$'a'$$ is defined as $$\,\,V\left( t \right) = {V_m}\,\cos \left( {\omega t} \right).\,\,\,$$ A symmetrical $$3\phi $$ fault occurs at centre of the line, i.e., at point $$'F'$$ at time 'to' the $$+ve$$ sequence impedance from source $${S_1}$$ to point $$'F'$$ equals $$(0.004 + j \,\,0.04)$$ $$p.u.$$ The wave form corresponding to phase $$'a'$$ fault current from bus $$X$$ reveals that decaying $$d.c.$$ offset current is $$-ve$$ and in magnitude at its maximum initial value. Assume that the negative sequence are equal to $$+ve$$ sequence impedances and the zero sequence $$(Z)$$ are $$3$$ times $$+ve$$ sequence $$(Z).$$
The $$rms$$ value of the ac component of fault current $$\,\left( {{{\rm I}_x}} \right)$$ will be

Voltage drop across the transmission line is given by the following equation:
$$$\left[ {\matrix{
{\Delta {V_a}} \cr
{\Delta {V_b}} \cr
{\Delta {V_c}} \cr
} } \right] = \left[ {\matrix{
{{Z_s}} & {{Z_m}} & {{Z_m}} \cr
{{Z_m}} & {{Z_s}} & {{Z_m}} \cr
{{Z_m}} & {{Z_m}} & {{Z_s}} \cr
} } \right]\left[ {\matrix{
{{i_a}} \cr
{{i_b}} \cr
{{i_c}} \cr
} } \right]$$$
Shunt capacitance of the line can be neglect. If the line has positive sequence impedance of $$15\,\,\Omega $$ and zero sequence in impedance of $$48\,\,\Omega ,$$ then the values of $${{Z_s}}$$ and $${{Z_m}}$$ will be

The synchronous generator transfers $$1.0$$ per unit of power to the infinite bus. The critical clearing time of circuit breaker is $$0.28$$ s. If another identical synchronous generator is connected in parallel to the existing generator and each generator is scheduled to supply $$0.5$$ per unit of power, then the critical clearing time of the circuit breaker will

An $$'a'$$ phase to ground fault with zero fault impedance occurs at the centre of the transmission line. Bus voltage at $$X$$ and line current from $$X$$ to $$F$$ for the phase $$'a',$$ are given by $${V_a}$$ Volts and $${{\rm I}_a}$$ Amperes, respectively. Then, the impedance measured by the ground distance relay located at the terminal $$X$$ of line $$XY$$ will be given by
$$y\left( t \right) = \int\limits_{ - \infty }^{ - 2t} {x\left( \tau \right)} d\tau .$$ The system will be
Statement-$$\left( {\rm I} \right)$$: Principle of superposition holds
Statement-$$\left( {\rm II} \right)$$: $$h\left( t \right) = 0$$ for $$t < 0$$
Which one of the following statements is correct?