GATE EE 2004
GATE EE
1
In the Schmitt trigger circuit shown in figure, if $${V_{CE}}\left( {sat} \right) = 0.1V,$$ the output logic low level $$\left( {{V_{OL}}} \right)$$ is


2
The input resistance $${R_{IN}}\left( { = {V_x}/{I_x}} \right)$$ of the circuit in the figure is


3
In the active filter circuit shown in figure, if $$Q=1,$$ a pair of poles will be realized with $${\omega _0}$$ equal to


4
The transconductance $${g_m}$$ of the transistor shown in figure is $$10$$ $$mS.$$ The value of input resistance $${R_{in}}$$ is


5
The value of $$R$$ for which the $$PMOS$$ transistor in Figure. $$Q$$ $$63$$ will be biased in linear region is


6
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is used as a power control switch by biasing it in the cutoff region (OFF state) or in the saturation region (ON state). In the ON state, for the BJT
7
Two perfectly matched silicon transistors are connected as shown in figure. The value of the current $${\rm I}$$ is


8
Assuming that the diodes are ideal in figure the current in the diode $${D_1}$$ is


9
The current through the zener diode in the given circuit is


10
The state variable description of a linear autonomous system is, $$\mathop X\limits^ \bullet = AX,\,\,$$ where $$X$$ is the two dimensional state vector and $$A$$ is the system matrix given by $$A = \left[ {\matrix{
0 & 2 \cr
2 & 0 \cr
} } \right].$$ The roots of the characteristic equation are
11
The open loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system is given as $$G\left( s \right) = {{as + 1} \over {{s^2}}}.$$. The value of $$‘a’$$ to give a phase margin of $${45^0}$$ is equal to
12
In the system shown in figure, the input $$x(t)$$ $$=$$ $$sin$$ $$t.$$ In the steady-state, the response $$y(t)$$ will be
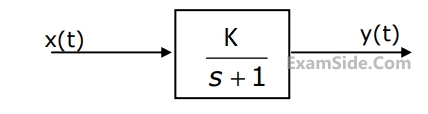

13
The Nyquist plot of loop transfer function $$G(s) H(s)$$ of a closed loop control system passes through the point $$(-1,j0)$$ in the $$G(s) H(s)$$ plane. The phase margin of the system is
14
A unity feedback system, having an open loop gain becomes stable when $$G\left( s \right)H\left( s \right) = {{K\left( {1 - s} \right)} \over {\left( {1 + s} \right)}}$$
15
For the equation, $${s^3} - 4{s^2} + s + 6 = 0$$ the number of roots in the left half of $$s$$ plane will be
16
The unit impulse response of a second order under-damped system starting from rest is given by $$c\left( t \right) = 12.5{e^{ - 6t}}\,\sin 8t,\,\,t \ge 0.$$
The steady-state value of the unit step response of the system is equal to
The steady-state value of the unit step response of the system is equal to
17
The block diagram of a closed loop control system is given by figure. The values of $$K$$ and $$P$$ such that the system has a damping ratio of $$0.7$$ and an undamped natural frequency $${\omega _n}$$ of $$5$$ rad/sec, are respectively equal to
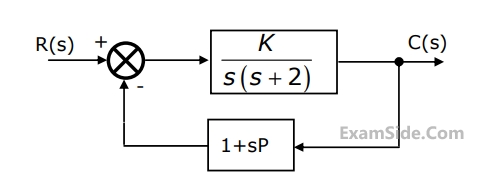

18
Consider the function $$F\left( s \right) = {5 \over {s\left( {{s^2} + 3s + 2} \right)}}$$ Where $$F(s)$$ is the Laplace transform of the function $$f(t).$$ The initial value of $$f(t)$$ is equal to
19
Consider the function $$F\left( s \right) = {5 \over {s\left( {{s^2} + 3s + 2} \right)}}$$ Where $$F(s)$$ is the Laplace transform of the function $$f(t).$$ The initial value of $$f(t)$$ is equal to
20
Consider the function $$F\left( s \right) = {5 \over {s\left( {{s^2} + 3s + 2} \right)}}$$ Where $$F(s)$$ is the Laplace transform of the function $$f(t).$$ The initial value of $$f(t)$$ is equal to
21
For the block diagram shown in figure, the transfer function $${{C\left( s \right)} \over {R\left( s \right)}}$$ is equal to


22
For a tachometer if $$\theta \left( t \right)$$ is the rotor displacement is radians, $$e\left( t \right)$$ is the output voltage and $${K_t}$$ is the tachometer constant in V/rad/sec, then the transfer function $${{E\left( s \right)} \over {\theta \left( s \right)}},$$ will be
23
The voltage comparator shown in Fig. can be used in the analog-to-digital conversion as


24
The digital circuit shown in figure generates a modified clock pulse at the output. Choose the correct output waveform form the options given below.


25
The digital circuit using two inverters shown in figure will act as


26
A digital circuit which compares two numbers $${A_3}{A_2}{A_1}{A_0},\,\,{B_3}{B_2}{B_1}{B_0}$$ is shown in Fig. To get output $$Y=0,$$ choose one pair of correct input numbers


27
The simplified form of the Boolean expression $$Y = \left( {\overline A BC + D} \right)\left( {\overline A D + \overline B \overline C } \right)$$ can be written as
28
In Fig., the value of the source voltage is


29
The $$Z$$ matrix of a $$2$$ $$-$$ port network is given by $$\left[ {\matrix{
{0.9} & {0.2} \cr
{0.2} & {0.6} \cr
} } \right].$$ The element $${Y_{22}}$$ vof the corresponding $$Y$$ matrix of the same network is given by
30
In Fig. the admittance values of the elements in Siemens are
$${Y_R} = 0.5 + j0,$$
$${Y_L} = 0 - j\,1.5,$$
$${Y_C} = 0 + j\,0.3$$ respectively.
The value of $${\rm I}$$ as a phasor when the voltage $$E$$ across the elements is $$10\angle {0^0}\,V$$ is
$${Y_R} = 0.5 + j0,$$
$${Y_L} = 0 - j\,1.5,$$
$${Y_C} = 0 + j\,0.3$$ respectively.
The value of $${\rm I}$$ as a phasor when the voltage $$E$$ across the elements is $$10\angle {0^0}\,V$$ is

31
The value of $$Z$$ in Fig., which is most appropriate to cause parallel resonance at $$500$$ $$Hz$$ is


32
In figure, the capacitor initially has a charge of $$10$$ Coulomb. The current in the circuit one second after the switch $$S$$ is closed will be


33
In Fig., $${R_a},\,\,{R_b},$$ and $${R_c}$$ are $$20\,\Omega ,\,\,10\,\Omega $$ and $$10\,\Omega $$ respectively. The resistances $${R_1},\,\,{R_2}$$ and $${R_3}$$ in $$\Omega $$ of an equivalent star - connection are


34
In Fig., the value of resistance $$R$$ in $$\Omega $$ is


35
A single-phase load is connected between $$R$$ and $$Y$$ terminals of a $$415$$ $$V,$$ symmetrical, $$3$$-phase, $$4$$-wire system with phase sequence $$RYB$$. A wattmeter is connected in the system as shown in figure. The power factor of the load is $$0.8 $$ lagging. The wattmeter will read


36
A $$CRO$$ probe has an impedance of $$500k\Omega $$ in parallel with a capacitance of $$10pF$$. The probe is used to measure the voltage between $$P$$ and $$Q$$ as shown in Fig. The measured voltage will be


37
The core flux in the $$CT$$ of above problem under the given operating condition is
38
A $$50$$ $$Hz,$$ bar primary $$CT$$ has a secondary with $$500$$ turns. The secondary supplies $$5A$$ current into a purely resistive burden of $$1\,\Omega $$. The magnetizing ampere-turns is $$200$$. The phase angle between the primary and secondary current is
39
A dc A-h meter is rated for 15 A, 250V. The meter constant is 14.4 A-sec/rev. The meter constant at rated voltage may be expressed as
40
The circuit in fig is used to measure the power consumed by the load. The current coil and the voltage coil of the watt meter have $$0.02$$ $$\Omega $$ and $$1000$$ $$\Omega $$ resistance respectively. The measured power compared to the load power will be


41
A moving coil of a meter has $$100$$ turns, and a length and depth of $$10$$ $$mm$$ and $$20$$ $$mm$$ respectively. It is positioned in a uniform radial flux density of $$200$$ $$mT.$$ The coil carries a current of $$50$$ $$mA.$$ The torque on the coil is
42
A moving iron ammeter produces a full scale torque of $$240$$ $$\,\mu Nm$$ with a deflection of $${120^ \circ }$$ at a current of $$10$$ $$A$$. The rate of change of self inductance $$\left( {\mu H/radian} \right)$$ of the instrument at full scale is
43
A galvanometer with a full scale current of $$10$$ $$mA$$ has a resistance of $$1000$$$$\Omega $$. The multiplying power (the ratio of measured current to galvanometer current) of a $$100$$$$\Omega $$ shunt with this galvanometer is
44
Two $$3$$-phase, $$Y$$-connected alternators are to be paralleled to a set of common bus bars. The armature has a per phase synchronous reactance of $$1.7\Omega $$ and negligible armature resistance. The line voltage of the first machines is adjusted to $$3300$$ $$V$$ and that of the second machine is adjusted to $$3200$$ $$V.$$ the machine voltages are in phase at the instant they are paralleled. Under this condition, the synchronizing current per phase will be
45
A hydraulic turbine having rated speed of $$250$$ $$rpm$$ is connected to a synchronous generator. In order to produce power at $$50$$ $$Hz,$$ the number of poles required in the generator are
46
A $$500$$ $$MW$$ $$3$$-phase $$Y$$-connected synchronous generator has a rated voltage of $$21.5kV$$ at $$0.85$$ $$pf.$$ The line current when operating at full load rated conditions will be
47
A $$400$$ $$V,$$ $$50$$ $$kVA,$$ $$0.8$$ $$pf$$ leading delta connected, $$50$$ $$Hz$$ synchronous machine has a synchronous reactance of $$2$$ $$ohm$$ and negligible armature resistance. The friction and windage losses are $$2$$ $$kW$$ and the core loss is $$0.8$$ $$kW.$$ The shaft is supplying $$9$$ $$kW$$ load at a power factor of $$0.8$$ leading. The line current drawn is
48
For a $$1.8$$ degree, $$2$$-phase bipolar stepper motor, the stepping rate is $$100$$ steps/second. The rotational speed of the motor in $$rpm$$ is
49
The synchronous speed for the seventh space harmonic $$mmf$$ wave of a $$3$$-phase, $$8$$ pole, $$50$$ $$Hz$$ induction machine is
50
A rotating electrical machine having its self-inductances of both the stator and
the rotor windings, independent of the rotor position will be definitely not develop
51
The following motor definitely has a permanent magnet rotor
52
For a given stepper motor, the following torque has the highest numerical value.
53
A single-phase, 230 V, 50 Hz, 4 pole, capacitor-start induction motor has the
following stand still impedances
Main winding Zm =6.0 + j4.0Ω
Auxiliary winding Za = 8.0 + j6.0Ω
The value of the starting capacitor required to produce 90° phase difference between the currents in the main and auxiliary windings will be
Main winding Zm =6.0 + j4.0Ω
Auxiliary winding Za = 8.0 + j6.0Ω
The value of the starting capacitor required to produce 90° phase difference between the currents in the main and auxiliary windings will be
54
A 400 V, 15 kW, 4 pole, 50 Hz, Y-connected induction motor has full load slip of
4%. The output torque of the machine at full load is
55
For a linear electromagnetic circuit, the following statement is true.
56
The direction of rotation of a 3-phase induction motor is clockwise when it is
supplied with 3-phase sinusoidal voltage having phase sequence A-B-C. For
counter clockwise rotation of the motor, the phase sequence of the power supply
should be
57
The type of single-phase induction motor having the highest power factor at full
load is
58
A 50 kVA, 3300/230 V single-phase transformers is connected as an
autotransformer shown in figure. The nominal rating of the autotransformer will
be


59
A 500 kVA, 3-phase transformer has iron loses of 300 W and full load copper
losses of 600 W. The percentage load at which the transformer is expected to
have maximum efficiency is
60
The resistance and reactance of a 100 kVA 11000|400 V, $$\triangle$$ - Y distribution
transformer are 0.02 and 0.07 pu respectively. The phase impedance of the
transformer referred to the primary is
61
A 8 pole, DC generator has a simplex wave-wound armature containing 32 coils
of 6 turns each. Its flux per pole is 0.06 Wb. The machine is running at 250 rpm.
The induced armature voltage is
62
The armature resistance of a permanent magnet dc motor is 0.8 $$\Omega$$. At no load, the
motor draws 1.5 A from a supply voltage of 25 V and runs at 1500 rpm. The
efficiency of the motor while it is operating on load at 1500 rpm drawing a
current of 3.5 A form the same source will be
63
The inductance of a long solenoid of length $$1000$$ $$mm$$ wound uniformly with $$3000$$ turns on a cylindrical paper tube of $$60$$ $$mm$$ diameter is
64
A parallel plate capacitor is shown in Fig. It is made of two square metal plates of $$400$$ $$mm$$ side. The $$14$$ $$mm$$ space between the plates is filled with two layers of dielectrics of $${\varepsilon _r} = 4,6\,\,mm$$ thick and $${\varepsilon _r} = 2,8\,\,mm$$ thick. Neglecting fringing of fields at the edges, the capacitance is


65
The area enclosed between the parabola $$y = {x^2}$$ and the straight line $$y=x$$ is _______.
66
The triac circuit shown in figure controls the $$ac$$ output power to the resistive load. The peak power dissipation in the load is


67
Figure shows a chopper operating from a $$100$$ $$V$$ $$dc$$ input. The duty ratio of the main switch $$S$$ is $$0.8.$$ The load is sufficiently inductive so that the load current is ripple free. The average current through the diode $$D$$ under steady state is


68
Figure shows a chopper. The device $${S_1}$$ is the main switching device. $${S_2}$$ is the auxiliary commutation device. $${S_1}$$ is rated for $$400V, 60A.$$ $${S_2}$$ is rated for $$400V, 30 A.$$ the load current is $$20$$ $$A.$$ The main device operates with a duty ratio of $$0.5.$$ The peak current through $${S_1}$$ is


69
The circuit in figure shows a $$3$$ $$-$$ phase half $$-$$ wave rectifier. The source is a symmetrical, $$3$$ $$-$$ phase four $$-$$ wire system. The line-to-line voltage of the source is $$100 V.$$ The supply frequency is $$400$$ $$Hz.$$ The ripple frequency at the output is


70
The circuit in figure shows a full-wave rectifier. The input voltage is $$230$$ $$V$$ $$(rms)$$ single-phase ac. The peak reverse voltage across the diodes $${D_1}$$ and $${D_2}$$ is


71
A $$MOSFET$$ rated for $$15 A,$$ carries a periodic current as shown in figure. The ON state resistance of the MOSFET is $$0.15$$ $$\Omega .$$ The average ON state loss in the $$MOSFET$$ is

72
The triggering circuit of a thyristor is shown in figure. The thyristor requires a gate current of $$10$$ $$mA,$$ for guaranteed turn-on. The value of $$R$$ required for the thyristor to turn on reliably under all conditions of $${V_b}$$ variation is


73
A bipolar junction transistor $$(BJT)$$ is used as a power control switch by biasing it in the cut-off region (OFF state) or in the saturation region (ON state). In the ON state, for the $$BJT.$$
74
A 50 Hz, 4-pole, 500 MVA, 22 kV turbo-generator is delivering rated megavolt-amperes at 0.8 power factor. Suddenly a fault occurs reducing is electric power output by 40%. Neglect losses and assume constant power input to the shaft. The accelerating torque in the generator in MNm at the time of fault will be
75
A $$110$$ $$kV,$$ single core coaxial, XLPE insulated power cable delivering power at $$50$$ $$Hz,$$ has a capacitance of $$125$$ $$nF/km.$$ If the dielectric loss tangent of XLPE is $$\,2\,\, \times \,\,{10^{ - 4}},$$ the dielectric power loss in this cable in $$W/km$$ is
76
The generalized circuit constants of a $$3$$-phase, $$220$$ $$kV$$ rated voltage, medium length transmission line are $$A = D = 0.936 + j\,0.016 = 0.936\angle {0.98^ \circ }$$
$$B = 33.5 + j138 = 142.0\angle {76.4^ \circ }\,\Omega $$
$$\,C = \left( { - 5.18 + j914} \right) \times \,{10^{ - 6}}\,\Omega $$
If the load at the receiving end is $$50$$ MW at $$220$$ $$kV$$ with a power factor of 0.9 lagging, then magnitude of line to line sending end voltage should be
$$B = 33.5 + j138 = 142.0\angle {76.4^ \circ }\,\Omega $$
$$\,C = \left( { - 5.18 + j914} \right) \times \,{10^{ - 6}}\,\Omega $$
If the load at the receiving end is $$50$$ MW at $$220$$ $$kV$$ with a power factor of 0.9 lagging, then magnitude of line to line sending end voltage should be
77
A $$800$$ $$kV$$ transmission line is having per phase line inductance of $$1.1$$ $$mH/km$$ and per phase line capacitance of $$11.68$$ $$nF/km.$$ Ignoring the length of the line, its ideal power transfer capability in $$MW$$ is
78
A lightning stroke discharges impulse current of $$10$$ kA (peak) on a $$400$$ kV transmission line having surge impedance of $$250\,\Omega $$. The magnitude of transient over-voltage traveling waves in either direction assuming equal distribution form the point of lightning strike will be
79
The phase sequence of the $$3$$-phase system shown in figure is


80
The rated voltage of a $$3$$-phase power system is given as
81
Total instantaneous power supplied by a $$3$$-phase ac supply to a balanced $$R$$-$$L$$ load is
82
A $$3$$-phase generator rated at $$110$$ MVA, $$11$$ kV is connected through circuit breakers to a transformer. The generator is having direct axis sub-transient reactance $$X'{'_d} = 19\% ,\,\,$$ transient reactance $$X{'_d} = 26\% \,\,$$ and synchronous reactance $$=130$$%. The generator is operating at no load and rated voltage when a three phase short circuit fault occurs between the breakers and the transformer. The magnitude of initial symmetrical rims current in the breakers will be
83
A new generator having $${E_g} = 1.4\,\angle {30^ \circ }\,$$ pu [ equivalent to ($$1.212 +j$$ $$0.70$$)pu ] and synchronous reactance $$'{X_s}'$$ of $$1.0$$ pu on the system base, is to be connected to a bus having voltage $${V_t}$$ in the existing power system. This existing power system can be represented by Thevenin's voltage $${E_{th}} = 0.9\angle {0^ \circ }\,\,$$ pu in series with Tjhevenin's impedance $${Z_{th}} = 0.25\angle {90^ \circ }\,\,$$ pu. The magnitude of the voltage $${V_t},$$ of the system in pu will be
84
For harnessing low variable water heads, the suitable hydraulic turbine with high percentage of reaction and runner adjustable vanes is
85
In thermal power plants, the pressure in the working fluid cycle is developed by
86
The transmission line distance protection relay having the property of being inherently directional is
87
A 500 MVA, 50 Hz, 3-phase turbo-generator produces power at 22 kV. Generator is Y-connected and its neutral is solidly grounded. Its sequence reactances are X1 = X2 = 0.15 and X0 = 0.05 pu. it is operating at rated voltage and disconnected from the rest of the system (no load). The magnitude of the sub-transient line current for single line ground fault at the generator terminal in pu will be
88
A 3-phase transmission line supplies $$\Delta - $$ connected load Z. The conductor $$'c'$$ of the line develops an open circuit fault as shown in figure. The currents in the lines are as shown on the diagram. The +ve sequence current component in line 'a' will be
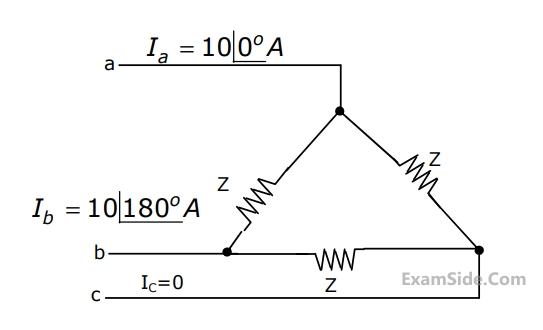

89
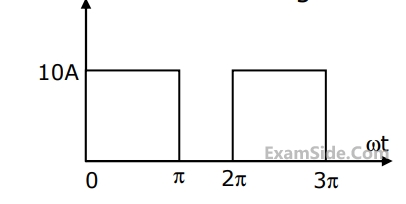
The $$rms$$ value of the periodic waveform given in Fig. is


90
In the system shown in Fig. the input $$x\left( t \right) = \sin t.$$ In the steady-state, the response $$y(t)$$ will be
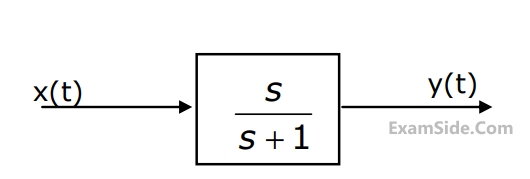

91
The rms value of the resultant current in a wire which carries a dc current of 10 A and a sinusoidal alternating current of peak value 20 A is