GATE EE
$$T\left( s \right) = {{{{ - s} \over {\left( {{R_1}C} \right)}}} \over {{s^2} + {{2s} \over {\left( {{R_3}C} \right)}} + {1 \over {\left( {R{R_3}{C^2}} \right)}}}}$$
where, $$R = {R_1}||{R_2}$$
If $${R_1} = 2k\Omega ,{R_2} = 2/3\,k\Omega ,\,\,{R_3} = 200\,k\Omega $$ and $$C = 0.1\,\,\mu F,$$ determine the center frequency $${\omega _0},$$ gain $${A_0}$$ and the $$Q$$ of the filter.



(a) Draw a rough sketch of the root locus plot; given that the complex roots ofthe characteristic equation move along a circle.
(b) As K increases, does the system become less stable? Justify your answer.
(c) Find the value of $$K$$ (if it exists) so that the damping $$\xi $$ of the complex closed loop poles is $$0.3.$$
Given : $$\,\left| {{G_1}\left( {j\omega } \right)} \right| \approx 1$$ when $$\omega = 0.446$$
(a) Determine the phase margin when $${\tau _D} = 0$$
(b) Comment in one sentence on the effect of dead time on the stability of the system.
(c) Determine the maximum value of dead time $${\tau _D}$$ for the closed-loop system to be stable.
Given : $${e^{AT}} = \left[ {\matrix{ {{e^{ - t}} + t{e^{ - t}}} & {t{e^{ - t}}} \cr { - t{e^{ - t}}} & {{e^{ - t}} - t{e^{ - t}}} \cr } } \right]$$
(a) Find a set of states $${x_1}\left( 1 \right)$$ and $${x_2}\left( 1 \right)$$ such that $${x_1}\left( 2 \right) = 2.$$
(b) Show that $$\,{\left( {s{\rm I} - A} \right)^{ - t}} = \Phi \left( s \right) = {1 \over \Delta }\left[ {\matrix{
{s + 2} & 1 \cr
{ - 1} & s \cr
} } \right];$$ $$\Delta = {\left( {s + 1} \right)^2}$$
(c) From $$\Phi \left( s \right),$$ find the matrix $$A$$.

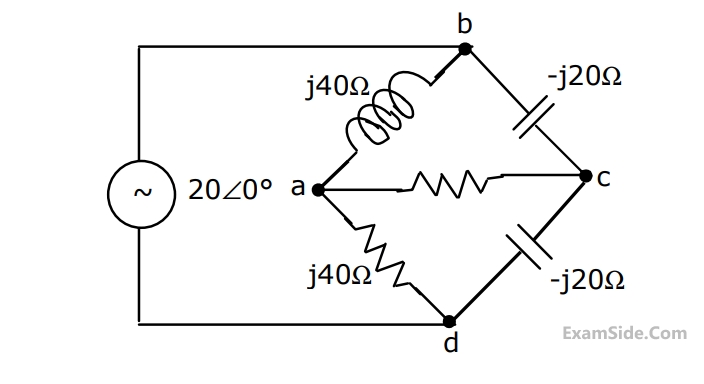

$${i_1} = 2{v_1} + {v_2}$$ and $${i_2} = {v_1} + {v_2}$$
Its impedance parameters $$\left( {{z_{11}},\,\,{z_{12}},\,\,{z_{21}},\,\,{z_{22}}} \right)$$ are given by

For economic operation, the generations $${P_1}$$ and $${P_2}$$ should be
$$x=0.05$$ $$ohms/km,$$ line charging susceptance $$y=3.0$$ micro-Siemens/k.
(a) Calculate the receiving end voltage on open circuit using justifiable assumptions.
(b) What load at the receiving end will result in a flat voltage profile on the line?
(c) If the flat voltage profile is to be achieved at $$1.2$$ times the loading in (b), what will be the nature and quantum of uniformly distributed compensation required?
(i) at the end of an interval
(ii) at the middle of an interval.
$$1.0$$ p.u. and $${Z_1} = {Z_2} = j0.1\,\,$$ p.u.,
$$\,{Z_0} = j0.05\,\,\,\,\,$$ p.u., for the alternator, then the required inductive reacttance for neutral grounding is
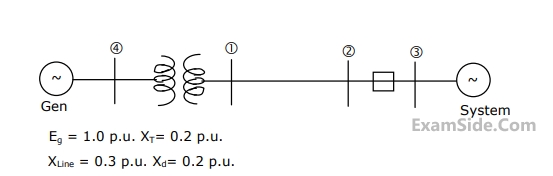
(i) No distance limitation related to steady state stability
(ii) No reactive power requirement from the system at the two terminals
(iii) No substantial effect on fault level of the two systems at the terminals inspite of the inter connection
(iv) no corona problems
The considerations which constitute advantages of HVDC transmission are