1
GATE CE 2023 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
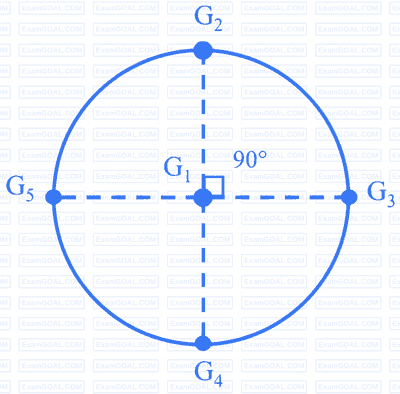
A catchment may be idealized as a circle of radius 30 km. There are five rain gauges, one at the center of the catchment and four on the boundary (equi-spaced), as shown in the figure (not to scale).
The annual rainfall recorded at these gauges in a particular year are given below.
$$ \begin{array}{|l|l|l|l|l|l|} \hline \text { Gauge } & \mathrm{G}_1 & \mathrm{G}_2 & \mathrm{G}_3 & \mathrm{G}_4 & \mathrm{G}_5 \\ \hline \text { Rainfall }(\mathrm{mm}) & 910 & 930 & 925 & 895 & 905 \\ \hline \end{array} $$
Using the Thiessen polygon method, what is the average rainfall (in mm, rounded off to two decimal places) over the catchment in that year? ________
Your input ____
2
GATE CE 2017 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
A catchment is idealized as a 25 km × 25 km square. It has five rain gauges, one at each
corner and one at the center, as shown in the figure.
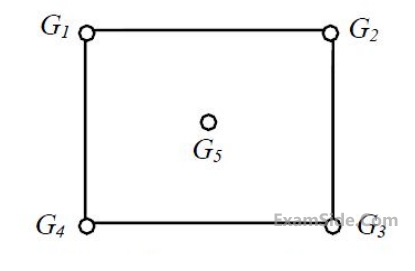 During a month, the precipitation at these gauges is measured as G1 = 300 mm, G2 = 285 mm, G3 = 272 mm, G4 = 290 mm and G5 = 288 mm. The average precipitation (in mm, up to one
decimal place) over the catchment during this month by using the Thiessen polygon method
is_______ .
During a month, the precipitation at these gauges is measured as G1 = 300 mm, G2 = 285 mm, G3 = 272 mm, G4 = 290 mm and G5 = 288 mm. The average precipitation (in mm, up to one
decimal place) over the catchment during this month by using the Thiessen polygon method
is_______ .
 During a month, the precipitation at these gauges is measured as G1 = 300 mm, G2 = 285 mm, G3 = 272 mm, G4 = 290 mm and G5 = 288 mm. The average precipitation (in mm, up to one
decimal place) over the catchment during this month by using the Thiessen polygon method
is_______ .
During a month, the precipitation at these gauges is measured as G1 = 300 mm, G2 = 285 mm, G3 = 272 mm, G4 = 290 mm and G5 = 288 mm. The average precipitation (in mm, up to one
decimal place) over the catchment during this month by using the Thiessen polygon method
is_______ .Your input ____
3
GATE CE 2015 Set 1
Numerical
+2
-0
In a catchment, there are four rain-gauge stations, P, Q, R, and S. Normal annual precipitation
values at these stations are 780 mm, 850 mm, 920 mm, and 980 mm, respectively. In the year
2013, stations Q, R, and S, were operative but P was not. Using the normal ratio method, the
precipitation at station P for the year 2013 has been estimated as 860 mm. If the observed
precipitation at stations Q and R for the year 2013 were 930 mm and 1010 mm, respectively;
what was the observed precipitation (in mm) at station S for that year?
Your input ____
Questions Asked from Precipitation and Frequency of Rainfall Data (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE CE Subjects
Construction Material and Management
Geomatics Engineering Or Surveying
Levelling Traversing Theodolites and Plane Table Surveying Measurement of Area, Volume and Theory of Errors and Survey Adjustment Curves Field Astronomy and Photogrammetric Surveying Basics of GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing Angular Measurements and Compass Survey Basic Concepts Linear Measurements and Chain Survey
Engineering Mechanics
Hydrology
Transportation Engineering
Strength of Materials Or Solid Mechanics
Reinforced Cement Concrete
Steel Structures
Environmental Engineering
Engineering Mathematics
Structural Analysis
Geotechnical Engineering
Origin of Soils Definitions and Properties of Soils Classification of Soils and Clay Mineralogy Effective Stress and Permeability Seepage Analysis Compaction of Soil Compressibility and Consolidation Shear Strength of Soil Stress Distribution of Soil Retaining Wall and Earth Pressure Stability of Slopes Shallow Foundation Pile Foundation Soil Stabilization
Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines
General Aptitude