Simple Stresses · Strength of Materials Or Solid Mechanics · GATE CE
Marks 1
A hanger is made of two bars of different sizes. Each bar has a square cross-section. The hanger is loaded by three-point loads in the mid vertical plane as shown in the figure. Ignore the self-weight of the hanger. What is the maximum tensile stress in N/mm2 anywhere in the hanger without considering stress concentration effects?

 If the shear strain $$\gamma_{xy}$$ at this point is expressed as 0.001k (in rad), the value of k is
If the shear strain $$\gamma_{xy}$$ at this point is expressed as 0.001k (in rad), the value of k is
 The following statements are made based on this diagram:
The following statements are made based on this diagram:I. Material A is more brittle than material B.
II. The ultimate strength of material B is more than that of A.
With reference to the above statements, which of the following applies?
Marks 2
A steel beam supported by three parallel pin-jointed steel rods is shown in the figure. The moment of inertia of the beam is $8 \times 10^7 \mathrm{~mm}^4$. Take modulus of elasticity of steel as 210 GPa . The beam is subjected to uniformly distributed load of $6.25 \mathrm{kN} / \mathrm{m}$, including its self-weight.
The axial force (in kN ) in the centre rod CD is___________ (round off to one decimal place).

A 5 cm long metal rod AB was initially at a uniform temperature of T0°C. Thereafter, temperature at both the ends are maintained at 0°C. Neglecting the heat transfer from the lateral surface of the rod, the heat transfer in the rod is governed by the one-dimensional diffusion equation $\rm\frac{\partial T}{\partial t}=D\frac{\partial^2T}{\partial x^2}$, where D is the thermal diffusivity of the metal, given as 1.0 cm2/s.
The temperature distribution in the rod is obtained as
$\rm T(x,t)=\Sigma_{n=1,3,5...}^{\infty}C_n\sin\frac{n\pi x}{5}e^{-\beta n^2t}$,
where x is in cm measured from A to B with 𝑥 = 0 at A, t is in s, 𝐶𝑛 are constants in °C, T is in °C, and β is in s−1 .
The value of β (in 𝑠−1 , rounded off to three decimal places) is ________.
Consider two linearly elastic rods HI and IJ. Each of length b, as shown in the figure. The rods are co-linear, and confined between two fixed supports at if and J. Both the rods are initially stress free. The coefficient of linear thermal expansion is a for both the rods. The temperature of the rod IJ is raised by $$\Delta$$T whereas the temperature of rod HI remains unchanged. An external horizontal force P is now applied at node I. It is given that a = 10$$-$$6 $$^\circ$$C$$-$$1, $$\Delta$$T = 50$$^\circ$$C, b = 2m, AE = 106N. The axial rigidities of the rods HI and U are 2 AE and AE, respectively.

To make the axial force in rod HI equal to zero, the value of the external force P (in N) is _________. (rounded off to the nearest integer).
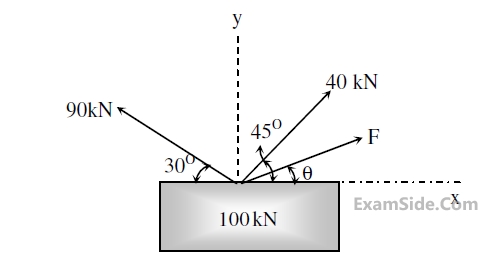
The axial movement of top surface of stepped column as shown in figure is
