GATE CSE
int f1(int n){
if(n == 0 || n == 1){
return n;
}
return (2 * f1(n - 1) + 3 * f1(n - 2));
}
int f2(int n){
int i;
int X[N], Y[N], Z[N];
X[0] = Y[0] = Z[0] = 0;
X[1] = 1; Y[1] = 2; Z[1] = 3;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++){
X[i] = Y[i - 1] + Z[i - 2];
Y[i] = 2 * X[i];
Z[i] = 3 * X[i];
}
return X[n];
}
Given a set S of n positive integers and a positive integer W, determine whether there is a subset of S Whose elements sum to W. An algorithm Q solves this problem in O(nW) time. Which of the following statements is false?
1. f(int Y[10], int x) {
2. int i, j, k;
3. i = 0; j = 9;
4. do {
5. k = (i + j) /2;
6. if( Y[k] < x) i = k; else j = k;
7. } while(Y[k] != x && i < j);
8. if(Y[k] == x) printf ("x is in the array ") ;
9. else printf (" x is not in the array ") ;
10. }1. f(int Y[10], int x) {
2. int i, j, k;
3. i = 0; j = 9;
4. do {
5. k = (i + j) /2;
6. if( Y[k] < x) i = k; else j = k;
7. } while(Y[k] != x && i < j);
8. if(Y[k] == x) printf ("x is in the array ") ;
9. else printf (" x is not in the array ") ;
10. }Which entry of the array X, if TRUE, implies that there is a subset whose elements sum to W?
Which of the following is valid for 2 <= i <= n and ai <= j <= W?
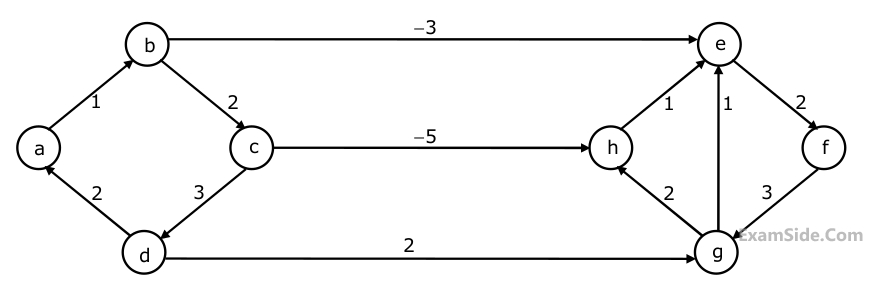 Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm when run from vertex a in the above graph, computes the correct shortest path distance to
Dijkstra's single source shortest path algorithm when run from vertex a in the above graph, computes the correct shortest path distance to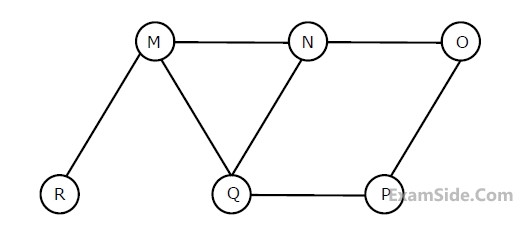
int f1(int n){
if(n == 0 || n == 1){
return n;
}
return (2 * f1(n - 1) + 3 * f1(n - 2));
}
int f2(int n){
int i;
int X[N], Y[N], Z[N];
X[0] = Y[0] = Z[0] = 0;
X[1] = 1; Y[1] = 2; Z[1] = 3;
for(i = 2; i <= n; i++){
X[i] = Y[i - 1] + Z[i - 2];
Y[i] = 2 * X[i];
Z[i] = 3 * X[i];
}
return X[n];
}
G(n) = n!
H(n) = nlogn
Which of the following statements about the asymptotic behaviour of f(n), g(n), and h(n) is true?
I. A programming language which does not permit global variables of any kind and has no nesting of procedures/functions, but permits recursion can be implemented with static storage allocation
II. Multi-level access link (or display) arrangement is needed to arrange activation records only if the programming language being implemented has nesting of procedures/functions
III. Recursion in programming languages cannot be implemented with dynamic storage allocation
IV. Nesting procedures/functions and recursion require a dynamic heap allocation scheme and cannot be implemented with a stack-based allocation scheme for activation records
V. Programming languages which permit a function to return a function as its result cannot be implemented with a stack-based storage allocation scheme for activation records
$$1.\,\,\,\,$$ Function locals and parameters
$$2.\,\,\,\,$$ Register saves and restores
$$3.\,\,\,\,$$ Instruction fetches
$$1.$$ It is useful in creating self relocating code
$$2.$$ If it is included in an Instruction Set Architecture, then an additional $$ALU$$ is required for effective address calculation
$$3.$$ The amount of increment depends on the size of the data item accessed.
$$1.$$ It must be a trap instruction
$$2.$$ It must be a privileged instruction
$$3.$$ An exception cannot be allowed to occur during execution of an $$RFE$$ instruction.
$$1.$$ Bypassing can handle all RAW hazards
$$2.$$ Register renaming can eliminate all register carried WAR hazards
$$3.$$ Control hazard penalties can be eliminated by dynamic branch prediction.
$$\eqalign{ & {{\rm I}_1}:\,\,ADD\,\,{R_2}\,\, \leftarrow \,\,{R_7} + {R_8} \cr & {{\rm I}_2}:\,\,SUB\,\,\,{R_4}\,\, \leftarrow \,\,{R_5} - {R_6} \cr & {{\rm I}_3}:\,\,ADD\,\,{R_1}\,\, \leftarrow \,\,{R_2} + {R_3} \cr & {{\rm I}_4}:\,\,STORE\,\,Memory\,\,\left[ {{R_4}} \right]\,\, \leftarrow \,\,{R_1} \cr & BRANCH\,\,to\,\,Label\,\,if\,\,{R_1} = = 0 \cr} $$
Which of the instructions $${{\rm I}_1},\,{{\rm I}_2},\,{{\rm I}_3}$$ or $${{\rm I}_4}$$ can legitimately occupy the delay slot without any other program modification?
$$1.$$ $$L1$$ must be a write-through cache
$$2.$$ $$L2$$ must be a write-through cache
$$3.$$ The associativity of $$L2$$ must be greater than that of $$L1$$
$$4.$$ The $$L2$$ cache must be at least as large as the $$L1$$ cache
43 36 92 87 11 4 71 13 14 is inserted into an initially empty hash table, the bins of which are indexed from zero to ten. What is the index of the bin into which the last record is inserted?
1.a b e f d g c
2.a b e f c g d
3.a d g e b c f
4.a d b c g e f
A Depth First Search (DFS) is started at node a. The nodes are listed in the order they are first visited. Which all of the above is (are) possible output(s)?

I. 81, 537, 102, 439, 285, 376, 305
II. 52, 97, 121, 195, 242, 381, 472
III. 142, 248, 520, 386, 345, 270, 307
IV. 550, 149, 507, 395, 463, 402, 270
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
I. 81, 537, 102, 439, 285, 376, 305
II. 52, 97, 121, 195, 242, 381, 472
III. 142, 248, 520, 386, 345, 270, 307
IV. 550, 149, 507, 395, 463, 402, 270
Suppose the BST has been unsuccessfully searched for key 273. Which all of the above sequences list nodes in the order in which we could have encountered them in the search?
struct node {
int value;
struct node *next;
};
Void rearrange (struct node *list ){
struct node *p, * q;
int temp;
if( !list || !list-> next) return;
p = list; q = list->next;
while (q) {
temp = p->value;
p-> value = q ->value;
q-> value = temp;
p = q-> next;
q = p ? p->next : 0;
}
}[ Notation: In the following NYO represents the action Y (R for read, W for write) performed by transaction N on object O. ]
(S1) 2RA 2WA 3RC 2WB 3WA 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
(S2) 3RC 2RA 2WA 2WB 3WA 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB 3WC
(S3) 2RZ 3RC 3WA 2WA 2WB 3WC 1RA 1RB 1WA 1WB
Which of the following statements is TRUE?R (P, Q, R1, R2, R3)
S (P, Q, S1, S2)
Where {P, Q} is the key for both schemas. Which of the following queries are equivalent?I. $$\Pi_P \left(R \bowtie S\right)$$
II. $$\Pi_P \left(R\right) \bowtie \Pi_P\left(S\right)$$
III. $$\Pi_P \left(\Pi_{P, Q} \left(R\right) \cap \Pi_{P,Q} \left(S\right) \right)$$
IV. $$\Pi_P \left(\Pi_{P, Q} \left(R\right) - \left(\Pi_{P,Q} \left(R\right) - \Pi_{P,Q} \left(S\right)\right)\right)$$
Which of the following tuple relational calculus expression(s) is/are equivalent to $$\forall t \in r \left(P\left(t\right)\right)$$?
I. $$\neg \exists t \in r \left(P\left(t\right)\right)$$II. $$\exists t \notin r \left(P\left(t\right)\right)$$
III. $$\neg \exists t \in r \left(\neg P\left(t\right)\right)$$
IV. $$\exists t \notin r \left(\neg P\left(t\right)\right)$$
Consider The Following Relational Scheme
Student (school-id, sch-roll-no, sname, saddress)
School (school-id, sch-name, sch-address, sch-phone)
Enrolment (school-id, sch-roll-no, erollno, examname)
ExamResult (Erollno, examname, marks)
SELECT sch-name, COUNT (*)
FROM School C, Enrolment E,
ExamResult R
WHERE E.school-id = C.school-id
AND E.examname = R.examname
AND E.erollno = R.erollno
AND R.marks = 100 AND S.school-id IN
(SELECT school-id
FROM student
GROUP BY school-id
HAVING COUNT (*) > 200)
GROUP BY school-id;Consider The Following Relational Scheme
Student (school-id, sch-roll-no, sname, saddress)
School (school-id, sch-name, sch-address, sch-phone)
Enrolment (school-id, sch-roll-no, erollno, examname)
ExamResult (Erollno, examname, marks)
Consider the following tuple relational calculus query
{ t | ∃E ∈ Enrolment t = E.school-id ∧
| { x | x ∈ ExamResult B.school-id =
t ∧ ( ∃B ∈ ExamResult B.erollno =
x.erollno ∧ B.examname = x.examname ∧
B.marks > 35 } | ÷ |
{ x | x ∈ Enrolment ∧ x.school-id = t }
| * 100 > 35 }$$A \to B,\,\,B \to C,\,\,C \to D$$ and $$D \to B.$$
The decomposition of $$R$$ into $$(A,B), (B,C)$$ and $$(B,D)$$
With in the following functional dependencies:
$${\rm I}.\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Title Author $$ \to $$ Catalog_no
$${\rm II}.\,\,\,\,$$ Catalog_no $$ \to $$ Title Author Publisher Year
$${\rm III}.\,\,\,\,$$ Publisher Title Year $$ \to $$ Price
Assume { Author, Title } is the key for both schemes. Which of the following statements is true?

Which of the following is a correct attribute set for one of the tables for the correct answer to the above question?

The minimum number of table needed to represent $$M,$$ $$N,$$ $$P, R1, R2$$ is

Then $${f_2}$$ is

Starting with the above tree, while there remains a node $$v$$ of degree two in the tree, add an edge between the two neighbours of $$v$$ and then remove $$v$$ from the tree. How many edges will remain at the end of the process?
$${n_3}$$ can be expressed as:
evaluates to
Which of the following recurrences does $${x_n}$$ satisfy?
The value of $${x_5}$$ is

$$\left[ {\matrix{ 1 & 0 \cr 0 & 0 \cr } } \right],\,\,\left[ {\matrix{ 0 & 1 \cr 0 & 0 \cr } } \right],\,\,\left[ {\matrix{ 1 & { - 1} \cr 1 & 1 \cr } } \right]\,\,and\,\,\left[ {\matrix{ { - 1} & 0 \cr 1 & { - 1} \cr } } \right]$$
$${x_1}\, + \,{x_2}\, + 2{x_3}\, = 1$$
$${x_1}\, + \,2 {x_2}\, + 3{x_3}\, = 2$$
$${x_1}\, + \,4{x_2}\, + a{x_3}\, = 4$$ has a unique solution. The only possible value (s) for $$\alpha $$ is/are
$$\left( {P \cap Q \cap R} \right) \cup \left( {{P^c} \cap Q \cap R} \right) \cup {Q^c} \cup {R^c}$$ is
$${\rm I}.$$ $${\rm P}\, \vee \sim Q$$
$${\rm I}{\rm I}.$$ $$ \sim \left( { \sim {\rm P} \wedge Q} \right)$$
$${\rm I}{\rm I}{\rm I}.$$ $$\left( {{\rm P} \wedge Q} \right) \vee \left( {{\rm P} \wedge \sim Q} \right) \vee \left( { \sim {\rm P} \wedge \sim Q} \right)$$
$${\rm I}V.$$ $$\left( {{\rm P} \wedge Q} \right) \vee \left( {{\rm P} \wedge \sim Q} \right) \vee \left( { \sim {\rm P} \wedge Q} \right)$$
Each finite state automation has an equivalent pushdown automation.
What is P $$P\,(A\, \cup \,B)\,$$?
$$S1$$ : Each row of $$M$$ can be represented as a linear combination of the other rows
$$S2$$ : Each column of $$M$$ can be represented as a linear combination of the other columns
$$S3$$ : $$MX$$ $$=$$ $$0$$ has a nontrivial solution
$$S4$$ : $$M$$ has an inverse
$$ * \,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Bits 30-31 are used to index into the first level page table
$$ * \,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Bits 21-29 are used to index into the second level page table
$$ * \,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Bits 12-20 are used to index into the third level page table, and
$$ * \,\,\,\,\,\,$$ Bits 0-11 are used as offset within the page
The number of bits required for addressing the next level page table (or page frame) in the page table entry of the first, second and third level page tables are respectively
P(s): s = s-1;
if s < 0 then wait;
V(s) : s = s-1;
ifs <= 0 then wakeup a process waiting on s;
P(s): Pb (Xb);
S = s - 1;
if(s < 0){
Vb(Xb);
Pb(Yb);
}
Else Vb (Xb);
V(s): Pb (Xb);
S = s + 1;
if(s <= 0) Vb(Yb);
Vb(Xb);
$${\rm I}.\,\,\,$$ It is useful in creating self-relocating code
$${\rm II}.\,\,\,$$ If it is included in an Instruction Set Architecture, then an additional $$ALU$$ is required for effective address calculation.
$${\rm III}.\,\,\,$$ The amount of increment depends on the size of the data item accessed
for (i = 0; i < n; i + +) fork ( ); #include < stdio.h >
int f(int x, int *py, int **ppz)
{
int y, z;
**ppz += 1;
z = **ppz;
*py += 2;
y = *py;
x += 3;
return x + y + z;
}
void main()
{
int c, *b, **a;
c = 4;
b = &c;
a = &b;
printf( "%d", f(c,b,a));
getchar();
}void recerse (void) {
int c;
if (?1) reverse() ;
?2
}
main {
printf ("Enter Text" );
printf("\n");
reverse() ;
printf("\n") ;
}I. A programming language which does not permit global variables of any kind and has no nesting of procedures/functions, but permits recursion can be implemented with static storage allocation
II. Multi-level access link (or display) arrangement is needed to arrange activation records only if the programming language being implemented has nesting of procedures/functions
III. Recursion in programming languages cannot be implemented with dynamic storage allocation
IV. Nesting procedures/functions and recursion require a dynamic heap allocation scheme and cannot be implemented with a stack-based allocation scheme for activation records
V. Programming languages which permit a function to return a function as its result cannot be implemented with a stack-based storage allocation scheme for activation records
$$1.$$ Whether the intersection of two regular languages is infinite
$$2.$$ Whether a given context-free language is regular
$$3.$$ Whether two push-down automata accept the same language
$$4.$$ Whether a given grammar is context-free
$$1.$$ Every left-recursive grammar can be converted to a right-recursive grammar and vice-versa
$$2.$$ All ε-productions can be removed from any context-free grammar by suitable transformations
$$3.$$ The language generated by a context-free grammar all of whose productions are of the form $$X \to w$$ or $$X \to wY$$ (where, $$w$$ is a string of terminals and $$Y$$ is a non terminal), is always regular
$$4.$$ The derivation trees of strings generated by a context-free grammar in Chomsky Normal Form are always binary trees
List-$${\rm I}$$
$$E)$$ Checking that identifiers are declared before their
$$F)$$ Number of formal parameters in the declaration of a function agrees with the number of actual parameters in a use of that function
$$G)$$ Arithmetic expression with matched pairs of parentheses
$$H)$$ Palindromes
List-$${\rm II}$$
$$P)$$ $$L = \left\{ {{a^n}{b^m}{c^n}{d^m}\,|\,n \ge 1,m \ge 1} \right\}$$
$$Q)$$ $$X \to XbX\,|\,XcX\,|\,dXf\,|g$$
$$R)$$ $$L = \left\{ {www\,|\,w \in \left( {a\,|\,b} \right){}^ * } \right\}$$
$$S)$$ $$X \to bXB\,|\,cXc\,|\,\varepsilon $$








Which of the following represents the product automation $$ZY$$?