GATE CSE
Let G be a connected undirected weighted graph. Consider the following two statements.
S1: There exists a minimum weight edge in G which is present in every minimum spanning tree of G.
S2: If every edge in G has distinct weight, then G has a unique minimum spanning tree. Which one of the following options is correct?
For constants a ≥ 1 and b > 1, consider the following recurrence defined on the non-negative integers :
$$T\left( n \right) = a.T\left( {\frac{n}{b}} \right) + f\left( n \right)$$
Which one of the following options is correct about the recurrence T(n)?
Consider the string abbccddeee. Each letter in the string must be assigned a binary code satisfying the following properties:
1. For any two letters, the code assigned to one letter must not be a prefix of the code assigned to the other letter.
2. For any two letters of the same frequency, the letter which occurs earlier in the dictionary order is assigned a code whose length is at most the length of the code assigned to the other letter.
Among the set of all binary code assignments which satisfy the above two properties, what is the minimum length of the encoded string?
Consider the following directed graph:

Which of the following is/are correct about the graph?
Consider the following ANSI C program:
int main() {
Integer x;
return 0;
}Which one of the following phases in a seven-phase C compiler will throw an error?
Consider the following augmented grammar with {#, @, <, >, a, b, c} as the set of terminals.
S' → S
S → S # cS
S → SS
S → S @
S → < S >
S → a
S → b
S → c
Let I0 = CLOSURE({S' → ∙ S}). The number of items in the set GOTO(GOTO(I0, <), <) is _______
Consider the following ANSI C code segment:
z = x + 3 + y -> f1 + y -> f2;
for (i = 0; i < 200; i = i + 2){
if (z > i) {
P = p + x + 3;
q = q + y -> f2;
} else {
p = p + y -> f2;
q = q + x + 3;
}
}
Assume that the variable y points to a struct (allocated on the heap) containing two fields f1 and f2, and the local variables x, y, z, p, g, and i are allotted registers. Common sub-expression elimination (CSE) optimization is applied on the code. The number of addition and dereference operations (of the form y -> f1 or y -> f2 ) in the optimized code, respectively, are:
For a statement S in a program, in the context of liveness analysis, the following sets are defined:
USE(S): the set of variables used in S
IN(S): the set of variables that are live at the entry of S
OUT(S): the set of variables that are live at the exit of S
Consider a basic block that consists of two statements, S1 followed by S2.
Which one of the following statements is correct?
Consider a computer network using the distance vector routing algorithm in its network layer. The partial topology of the network is as shown below.

The objective is to find the shortest-cost path from the router R to routers P and Q. Assume that R does not initially know the shortest routes to P and Q. Assume that R has three neighbouring routers denoted as X, Y, and Z. During one iteration, R measures its distance to its neighbours X, Y, and Z as 3, 2, and 5, respectively. Router R gets routing vectors from its neighbours that indicate that the distance to router P from routers X, Y, and Z are 7, 6, and 5, respectively. The routing vector also indicates that the distance to router Q from routers X, Y, and Z are 4, 6, and 8, respectively. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct with respect to the new routing table of R, after updation during this iteration ?
Assume a two-level inclusive cache hierarchy, L1 and L2, where L2 is the larger of the two. Consider the following statements.
S1 : Read misses in a write through L1 cache do not result in writebacks of dirty lines to the L2.
S2 : Write allocate policy must be used in conjunction with write through caches and no-write allocate policy is used with writeback caches.
Which of the following statements is correct?
Consider a pipelined processor with 5 stages, Instruction Fetch (IF), Instruction Decode (ID), Execute (EX), Memory Access (MEM), and Write Back (WB). Each stage of the pipeline, except the EX stage, takes one cycle. Assume that the ID stage merely decodes the instruction and the register read is performed in the EX stage. The EX stage takes one cycle for ADD instruction and two cycles for MUL instruction. Ignore pipeline register latencies.
Consider the following sequence of 8 instructions:
ADD, MUL, ADD, MUL, ADD, MUL, ADD, MUL
Assume that every MUL instruction is data-dependent on the ADD instruction just before it and every ADD instruction (except the first ADD) is data-dependent on the MUL instruction just before it. The speedup is defined as follows:
$$Speedup = \frac{{Execution{\:}time{\:}without{\:}operand{\:}forwarding}}{{Execution{\:}time{\:}with{\:}operand{\:}forwarding}}$$
The Speedup achieved in executing the given instruction sequence on the pipelined processor (rounded to 2 decimal places) is _______
Consider a complete binary tree with 7 nodes. Let A denote the set of first 3 elements obtained by performing Breadth-First Search (BFS) starting from the root. Let B denote the set of first 3 elements obtained by performing Depth-First Search (DFS) starting from the root.
The value of |A - B| is _______
The relation scheme given below is used to store information about the employees of a company, where empId is the key and deptId indicates the department to which the employee is assigned. Each employee is assigned to exactly one department.
emp(empId, name, gender, salary, deptId)
Consider the following SQL query:
select deptId, count(⋆)
from emp
where gender = "female" and salary > (select avg(salary) from emp)
group by deptId;
The above query gives, for each department in the company, the number of female employees whose salary is greater than the average salary of
Consider the following statements S1 and S2 about the relational data model:
S1: A relation scheme can have at most one foreign key.
S2: A foreign key in a relation scheme R cannot be used to refer to tuples of R.
Which one of the following choices is correct?
Suppose the following functional dependencies hold on a relation U with attributes P, Q, R, S, and T :
P → QR
RS → T
Which of the following functional dependencies can be inferred from the above functional dependencies?
Let S be the following schedule of operations of three transactions T1, T2 and T3 in a relational database system:
R2(Y), R1(X), R3(Z), R1(Y), W1(X), R2(Z), W2(Y), R3(X), W3(Z)
Consider the statements P and Q below:
P: S is conflict-serializable.
Q: If T3 commits before T1 finishes, then S is recoverable.
Which one of the following choices is correct?
Which one of the following circuits implements the Boolean function given below?
f(x, y, z) = m0 + m1 + m3 + m4 + m5 + m6, where mi is the ith minterm.
The format of the single-precision floating-point representation of a real number as per the IEEE 754 standard is as follows:
|
sign |
exponent |
mantissa |
Which one of the following choices is correct with respect to the smallest normalized positive number represented using the standard?
Suppose we want to design a synchronous circuit that processes a string of 0’s and 1’s. Given a string, it produces another string by replacing the first 1 in any subsequence of consecutive 1’s by a 0. Consider the following example.
Input sequence : 00100011000011100
Output sequence : 00000001000001100
A Mealy Machine is a state machine where both the next state and the output are functions of the present state and the current input.
The above mentioned circuit can be designed as a two-state Mealy machine. The states in the Mealy machine can be represented using Boolean values 0 and 1. We denote the current state, the next state, the next incoming bit, and the output bit of the Mealy machine by the variables s, t, b and y respectively.
Assume the initial state of the Mealy machine is 0.
What are the Boolean expressions corresponding to t and y in terms of s and b ?
Consider a Boolean function f(w, x, y, z) such that
f(w, 0, 0, z) = 1
f(1, x, 1, z) = x + z
f(w, 1, y, z) = wz + y
The number of literals in the minimal sum-of-products expression of f is ______
Consider the following sets, where n > 2:
S1: Set of all n x n matrices with entries from the set {a, b, c}
S2: Set of all functions from the set {0,1, 2, ..., n2 — 1} to the set {0, 1, 2}
Which of the following choice(s) is/are correct?
Choose the correct choice(s) regarding the following propositional logic assertion S:
S : ((P ∧ Q)→ R)→ ((P ∧ Q)→ (Q → R))
In an examination, a student can choose the order in which two questions (QuesA and QuesB) must be attempted.
- If the first question is answered wrong, the student gets zero marks.
- If the first question is answered correctly and the second question is not answered correctly, the student gets the marks only for the first question.
- If both the questions are answered correctly, the student gets the sum of the marks of the two questions.
The following table shows the probability of correctly answering a question and the marks of the question respectively.
| question | Probability of answering correctly | marks |
| QuesA | 0.8 | 10 |
| QuesB | 0.5 | 20 |
Assuming that the student always wants to maximize her expected marks in the examination, in which order should she attempt the questions and what is the expected marks for that order (assume that the questions are independent)?
For two n-dimensional real vectors P and Q, the operation s(P, Q) is defined as follows:
$$s\left( {P,\;Q} \right) = \mathop \sum \limits_{i = 1}^n \left( {p\left[ i \right].Q\left[ i \right]} \right)$$
Let L be a set of 10-dimensional non-zero vectors such that for every pair of distinct vectors P, Q ∈ L, s(P, Q) = 0. What is the maximum cardinality possible for the set L ?
In a directed acyclic graph with a source vertex s, the quality-score of a directed path is defined to be the product of the weights of the edges on the path. Further, for a vertex v other than s, the quality-score of v is defined to be the maximum among the quality-scores of all the paths from s to v. The quality-score of s is assumed to be 1.

The sum of the quality-scores of all the vertices in the graph shown above is ______
Consider a computer system with multiple shared resource types, with one instance per resource type. Each instance can be owned by only one process at a time. Owning and freeing of resources are done by holding a global lock (L). The following scheme is used to own a resource instance:
function OWNRESOURCES(Resource R)
Acquire lock L / / a global lock
if R is available then
Acquire R
Release lock L
else
if R is owned by another process P then
Terminate P, after releasing all resources owned by P
Acquire R
Restart P
Release lock L
end if
end if
end function
Which of the following choice(s) about the above scheme is/are correct?
Consider the following multi-threaded code segment (in a mix of C and pseudocode), invoked by two processes P1 and P2, and each of the processes spawns two threads T1 and T2:
int x = 0; // global
Lock L1; // global
main() {
create a thread to execute foo(); // Thread T1
create a thread to execute foo(); // Thread T2
wait for the two threads to finish execution;
print (x);}
foo() {
int y = 0;
Acquire L1;
x = x + 1;
y = y + 1;
Release L1;
print (y); }
Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ?
Consider a three-level page table to translate a 39-bit virtual address to a physical address as shown below.

The page size is 4 KB (1 KB = 210 bytes) and page table entry size at every level is 8 bytes. A process P is currently using 2 GB (1 GB = 230 bytes) virtual memory which is mapped to 2 GB of physical memory. The minimum amount of memory required for the page table of P across all levels is _______ KB.
Consider the following ANSI C function:
int SomeFunction (int x, int y)
{
if ( (x == 1) I I (y == 1)) return 1;
if (x == y) return x;
if (x > y) return SomeFunction(x - y, y);
if (y > x) return SomeFunction(x, y - x);
}
The value returned by SomeFunction(15, 255) is _______.
Consider the following ANSI C program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node{
int value;
struct Node ⋆next;};
int main(){
struct Node ⋆boxE, ⋆head, ⋆boxN; int index = 0;
boxE = head = (struct Node ⋆) malloc (sizeof(struct Node));
head -> value = index;
for (index = 1; index <=3; index++){
boxN = (struct Node ⋆) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
boxE -> next = boxN;
boxN -> value = index;
boxE = boxN; }
for (index = 0; index <= 3; index++) {
printf("value at index %d is %d\m", index, head -> value);
head = head -> next;
printf("value at index %d is %d\n", index + 1, head -> value);}}
Which one of the statement below is correct about the program ?
Consider the following ANSI C program
#include <stdio.h>
int foo(int x, int y, int q)
{
if ((x <= 0 && (y <= 0))
return q;
if (x <= 0)
return foo(x, y - q, q);
if (y <= 0)
return foo(x - q, y, q);
return foo (x, y - q, q) + foo(x - q, y, q);
}
int main()
(
int r = foo(15, 15, 10);
printf("%d", r);
return 0;
}
The output of the program upon execution is ________
Consider the following ANSI C program.
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int arr[4][5];
int i, j;
for(i =0; i<4; i++){
for (j =0; j<5; j++){
arr [i][j] = 10*i + j;
}
}
print("%d", *(arr[1] + 9));
return 0;
}
What is the output of the above program?
Consider the following deterministic finite automaton (DFA).

The number of strings of length 8 accepted by the above automaton is __________
For a string w, we define wR to be the reverse of w. For example, if w = 01101 then wR = 10110.
Which of the following languages is/are context-free?
Consider the following two statements about regular languages:
S1: Every infinite regular language contains an undecidable language as a subset.
S2: Every finite language is regular.
Which one of the following choices is correct?
General Aptitude
Which one of the following statements is the CORRECT inference of the above passage?
Which one of the following options maintains a similar logical relation in the above?

A jigsaw puzzle has 2 pieces. One of the pieces is shown above. Which one of the given option for the missing piece when assembled will form a rectangle? The piece can be moved. rotated or flipped to assemble with the above piece.
Observation I : S is taller than R.
Observation II : Q is the shortest of all.
Observation III : U is taller than only one student.
IV : T is taller than S but is not the tallest.
The number of students that are taller than R is the same as the number of students shorter than ________.
The total number of students in all the three classes in the beginning was :
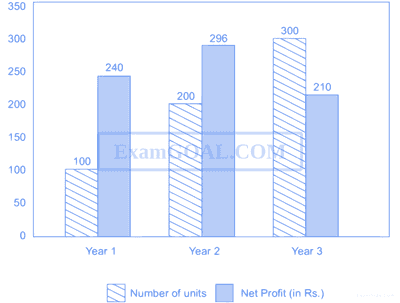
The number of units of a product sold in three different years and the respective net profits are presented in the figure above. The cost/unit in year 3 was Rs. 1, which was half the cost/unit in year 2. The cost/unit in year 3 was one-third of the cost/unit in year 1. Taxes were paid on the selling price at 10%, 13% and 15% respectively for the three years. Net profit is calculated as the difference between the selling price and the sum of cost and taxes paid in that year.
The ratio of the selling price in Year 2 to the selling price in Year 3 is _______
