1
GATE CE 2014 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
The beam of an overall depth $$250$$ $$mm$$ (shown below) is used in a building subjected to two different thermal environments. The temperatures at the top and bottom surfaces of the beam are $${36^ \circ }C$$ and $${72^ \circ }C$$ respectively. Considering coefficient of thermal expansion $$\left( \alpha \right)$$ as $$1.50 \times {10^{ - 5}}\,\,$$ per$${}^ \circ C,$$ the vertical deflection of the beam (in $$mm$$) at its mid-span due to temperature gradient is ______________


Your input ____
2
GATE CE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A beam with cross-section given below is subjected to a positive bending moment (causing compression at the top) of $$16$$ $$kN$$-$$m$$ acting around the horizontal axis. The tensile force acting on the hatched area of the cross-section is
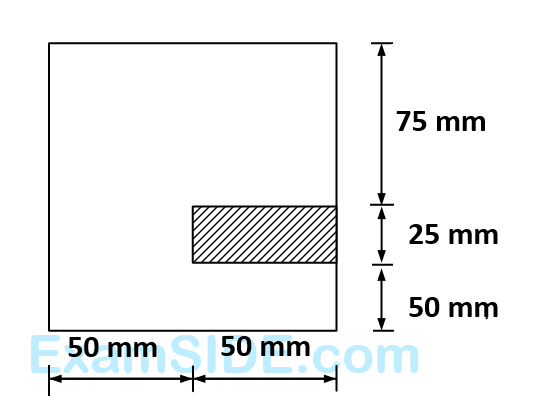

3
GATE CE 2003
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A simply supported beam of uniform rectangular cross-section of width $$b$$ and depth $$h$$ is subjected to linear temperature gradient, $${0^ \circ }$$ at the top $${T^ \circ }$$ at the bottom, as shown in the figure. The coefficient of linear expansion of the beam material is $$\alpha .$$ This resulting vertical deflection at the mid-span of the beam is


4
GATE CE 1992
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The maximum bending stress induced in a steel wire of modulus of elasticity $$200$$ $$kN/m{m^2}$$ and diameter $$1$$ $$mm$$ when wound on a drum of diameter $$1$$ $$m$$ is approximately equal to
Questions Asked from Pure Bending (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE CE Subjects
Engineering Mechanics
Strength of Materials Or Solid Mechanics
Structural Analysis
Construction Material and Management
Reinforced Cement Concrete
Steel Structures
Geotechnical Engineering
Origin of Soils Definitions and Properties of Soils Classification of Soils and Clay Mineralogy Effective Stress and Permeability Seepage Analysis Compaction of Soil Compressibility and Consolidation Shear Strength of Soil Stress Distribution of Soil Retaining Wall and Earth Pressure Stability of Slopes Shallow Foundation Pile Foundation Soil Stabilization
Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines
Hydrology
Geomatics Engineering Or Surveying
Levelling Traversing Theodolites and Plane Table Surveying Measurement of Area, Volume and Theory of Errors and Survey Adjustment Curves Field Astronomy and Photogrammetric Surveying Basics of GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing Angular Measurements and Compass Survey Basic Concepts Linear Measurements and Chain Survey
Environmental Engineering
Transportation Engineering
Engineering Mathematics
General Aptitude