1
GATE CE 2022 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
Consider two linearly elastic rods HI and IJ. Each of length b, as shown in the figure. The rods are co-linear, and confined between two fixed supports at if and J. Both the rods are initially stress free. The coefficient of linear thermal expansion is a for both the rods. The temperature of the rod IJ is raised by $$\Delta$$T whereas the temperature of rod HI remains unchanged. An external horizontal force P is now applied at node I. It is given that a = 10$$-$$6 $$^\circ$$C$$-$$1, $$\Delta$$T = 50$$^\circ$$C, b = 2m, AE = 106N. The axial rigidities of the rods HI and U are 2 AE and AE, respectively.

To make the axial force in rod HI equal to zero, the value of the external force P (in N) is _________. (rounded off to the nearest integer).
Your input ____
2
GATE CE 2016 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
An elastic isotropic body is in a hydrostatic state of stress as shown in the figure. For no
change in the volume to occur, what should be its Poisson's ratio?
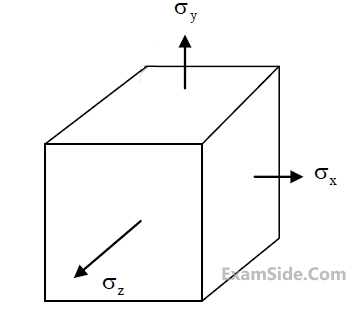

3
GATE CE 2014 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A box of weight 100 kN shown in the figure is to be lifted without swinging. If all forces are
coplanar, the magnitude and direction ($$\theta$$) of the force (F) with respect to x-axis should be
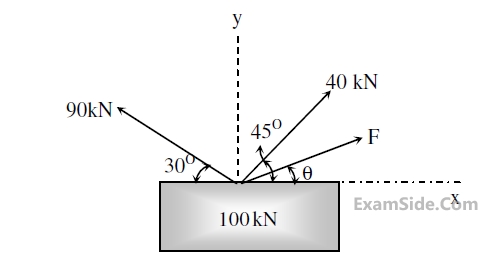

4
GATE CE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A metal bar of length 100mm is inserted between two rigid supports and its
temperature is increased by $$10^o$$C. If the coefficient of thermal expansion is 12 x$$10^{-6}$$ per $$^o$$C and the Young’s modulus is 2 x $$10^{5}$$ MPa, the stress in the bar is
Questions Asked from Simple Stresses (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE CE Subjects
Engineering Mechanics
Strength of Materials Or Solid Mechanics
Structural Analysis
Construction Material and Management
Reinforced Cement Concrete
Steel Structures
Geotechnical Engineering
Origin of Soils Definitions and Properties of Soils Classification of Soils and Clay Mineralogy Effective Stress and Permeability Seepage Analysis Compaction of Soil Compressibility and Consolidation Shear Strength of Soil Stress Distribution of Soil Retaining Wall and Earth Pressure Stability of Slopes Shallow Foundation Pile Foundation Soil Stabilization
Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machines
Hydrology
Geomatics Engineering Or Surveying
Levelling Traversing Theodolites and Plane Table Surveying Measurement of Area, Volume and Theory of Errors and Survey Adjustment Curves Field Astronomy and Photogrammetric Surveying Basics of GIS, GPS and Remote Sensing Angular Measurements and Compass Survey Basic Concepts Linear Measurements and Chain Survey
Environmental Engineering
Transportation Engineering
Engineering Mathematics
General Aptitude