1
GATE EE 2017 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The bus admittance matrix for a power system network is
$$$\left[ {\matrix{
{ - j39.9} & {j20} & {j20} \cr
{j20} & { - j39.9} & {j20} \cr
{j20} & {j20} & { - j39.9} \cr
} } \right]\,pu.$$$
There is a transmission line connected between buses $$1$$ and $$3,$$ which is represented by the circuit shown in figure.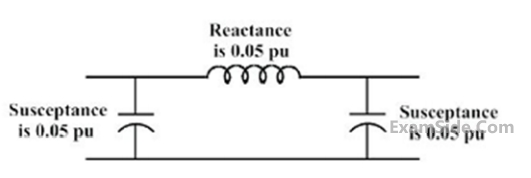
There is a transmission line connected between buses $$1$$ and $$3,$$ which is represented by the circuit shown in figure.

If this transmission line is removed from service what is the modified bus admittance matrix?
2
GATE EE 2017 Set 1
Numerical
+1
-0
A 10-bus power system consists of four generator buses indexed as G1, G2, G3, G4 and six load buses indexed as L1, L2, L3, L4, L5, L6. The generator bus G1 is considered as slack bus, and the load buses L3 and L4 are voltage controlled buses. The generator at bus G2 cannot supply the required reactive power demand, and hence it is operating at its maximum reactive power limit. The number of non-linear equations required for solving the load flow problem using Newton-Raphson method in polar form is ____________.
Your input ____
3
GATE EE 2017 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
A source is supplying a load through a 2-phase, 3-wire transmission system as shown in figure
below. The instantaneous voltage and current in phase-a are $$v_{an}=220\sin\left(100\mathrm{πt}\right)\;V$$ and
$$i_a=10\sin\left(100\mathrm{πt}\right)\;A$$, respectively. Similarly for phase-b the instantaneous voltage and current
are $$v_{bn}=220\cos\left(100\mathrm{πt}\right)\;V$$ and $$i_b=10\cos\left(100\mathrm{πt}\right)\;A$$, respectively.
 The total instantaneous power flowing form the source to the load is
The total instantaneous power flowing form the source to the load is
 The total instantaneous power flowing form the source to the load is
The total instantaneous power flowing form the source to the load is4
GATE EE 2017 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A load is supplied by a $$230$$ $$V,$$ $$50$$ $$Hz$$ source. The active power $$P$$ and the reactive power $$Q$$ consumed by the load are such that $$1$$ $$kW$$ $$ \le P \le 2\,kW\,\,$$ and $$\,1\,\,kVAR \le 2\,\,kVAR.\,\,$$ A capacitor connected across the load for power factor correction generates $$1$$ $$kVAR$$ reactive power. The worst case power factor after power factor correction is
Paper analysis
Total Questions
Analog Electronics
3
Control Systems
7
Digital Electronics
3
Electric Circuits
4
Electrical and Electronics Measurement
3
Electrical Machines
7
Electromagnetic Fields
3
Engineering Mathematics
6
Power Electronics
5
Power System Analysis
7
Signals and Systems
4
More papers of GATE EE
GATE EE 2025
GATE EE 2024
GATE EE 2023
GATE EE 2022
GATE EE 2021
GATE EE 2020
GATE EE 2019
GATE EE 2018
GATE EE 2017 Set 2
GATE EE 2017 Set 1
GATE EE 2016 Set 2
GATE EE 2016 Set 1
GATE EE 2015 Set 1
GATE EE 2015 Set 2
GATE EE 2014 Set 2
GATE EE 2014 Set 3
GATE EE 2014 Set 1
GATE EE 2013
GATE EE 2012
GATE EE 2011
GATE EE 2010
GATE EE 2009
GATE EE 2008
GATE EE 2007
GATE EE 2006
GATE EE 2005
GATE EE 2004
GATE EE 2003
GATE EE 2002
GATE EE 2001
GATE EE 2000
GATE EE 1999
GATE EE 1998
GATE EE 1997
GATE EE 1996
GATE EE 1995
GATE EE 1994
GATE EE 1993
GATE EE 1992
GATE EE 1991
GATE EE
Papers
2025
2024
2023
2022
2021
2020
2019
2018
2013
2012
2011
2010
2009
2008
2007
2006
2005
2004
2003
2002
2001
2000
1999
1998
1997
1996
1995
1994
1993
1992
1991