 Consider the correct spanning tree for the previous question. Let host H1 send out a broadcast ping packet. Which of the following options represents the correct forwarding table on B3?
Consider the correct spanning tree for the previous question. Let host H1 send out a broadcast ping packet. Which of the following options represents the correct forwarding table on B3?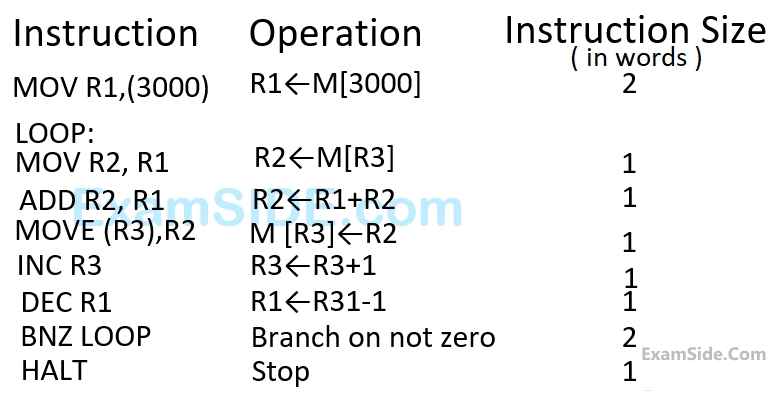
Assume that the content of memory location $$3000$$ is $$10$$ and the content of the register $$R3$$ is $$2000$$. The content of each of the memory locations from $$2000$$ to $$2010$$ is $$100.$$ The program is loaded from the memory location $$1000.$$ All the numbers are in decimal.
Assume that the memory is word addressable. The number of memory references for accessing the data in executing the program completely is

Assume that the content of memory location $$3000$$ is $$10$$ and the content of the register $$R3$$ is $$2000$$. The content of each of the memory locations from $$2000$$ to $$2010$$ is $$100.$$ The program is loaded from the memory location $$1000.$$ All the numbers are in decimal.
Assume that the memory is word addressable. After the execution of this program, the content of memory location $$2010$$ is

Assume that the content of memory location $$3000$$ is $$10$$ and the content of the register $$R3$$ is $$2000$$. The content of each of the memory locations from $$2000$$ to $$2010$$ is $$100.$$ The program is loaded from the memory location $$1000.$$ All the numbers are in decimal.
Assume that the memory is byte addressable and the word size is $$32$$ bits. If an interrupt occurs during the execution of the instruction $$''INC$$ $$R3'',$$ what return address will be pushed on to the stack?



