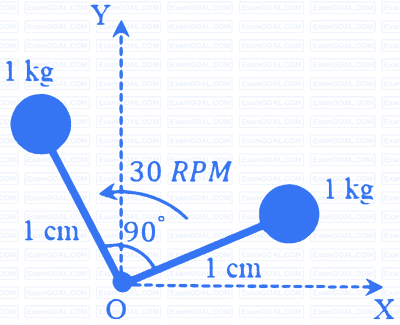
A rigid body in the X-Y plane consists of two point masses (1 kg each) attached to the ends of two massless rods, each of 1 cm length, as shown in the figure. It rotates at 30 RPM counter-clockwise about the Z-axis passing through point O. A point mass of √2 kg, attached to one end of a third massless rod, is used for balancing the body by attaching the free end of the rod to point O. The length of the third rod is ______ cm.
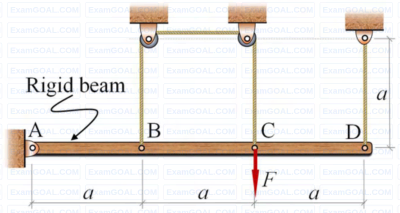
A rigid beam AD of length 3a = 6 m is hinged at frictionless pin joint A and supported by two strings as shown in the figure. String BC passes over two small frictionless pulleys of negligible radius. All the strings are made of the same material and have equal cross-sectional area. A force F = 9 KN is applied at C and the resulting stresses in the strings are within linear elastic limit. The self-weight of the beam is negligible with respect to the applied load. Assuming small deflections, the tension developed in the string at C is KN (round off to 2 decimal places).
The lengths of members BC and CE in the frame shown in the figure are equal. All the members are rigid and lightweight, and the friction at the joints is negligible. Two forces of magnitude Q > 0 are applied as shown, each at the mid-length of the respective member on which it acts.

Which one or more of the following members do not carry any load (force)?
Consider a steady flow through a horizontal divergent channel, as shown in the figure, with the supersonic flow at the inlet. The direction of flow is from left to right.
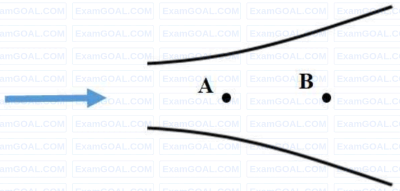
Pressure at location B is observed to be higher than that at an upstream location A. Which among the following options can be the reason?