A point mass ' $m$ ' attached at one end of a massless, inextensible string of length ' $l$ ' performs a vertical circular motion and the string rotates in vertical plane, as shown in the diagram. The increase in the centripetal acceleration of the point mass when it moves from point A to point C is
[ $\mathrm{g}=$ acceleration due to gravity.]

A body cools from $80^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to $50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ in 5 min . In the next time of ' t ' in, the body continues to cool from $50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to $30^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$. The total time taken by the body to cool from $80^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to $30^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ is [The temperature of the surroundings is $20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$.]
A square of side ' $L$ ' metre lies in $x-y$ plane in a region where the magnetic field is $\overline{\mathrm{B}}$ and $\vec{B}=B_0(2 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}+4 \hat{k})$, where $B_0$ is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square (in weber) is
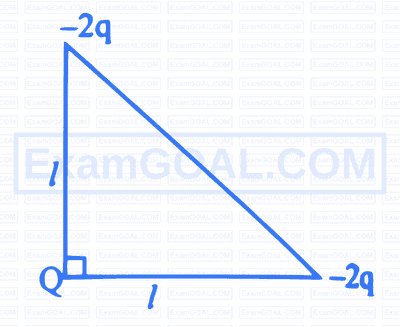
Three charges $Q(-2 q)$ and $(-2 q)$ are placed at the vertices of an isosceles right angled triangle as shown in figure. The net electrostatic potential energy is zero if $Q$ is equal to