On a photosensitive material, when frequency of incident radiation is increased by $20 \%$, maximum kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons increases from 0.4 eV to 0.7 eV . The work function of the material is
A parallel plate capacitor with plate area A and plate separation $d$ is charged by constant current $I$. A plane surface of area $\frac{\mathrm{A}}{2}$, parallel to the plates is drawn simultaneously between the plates. The displacement current through this area is
A liquid drop having surface energy $E$ is sprayed into 512 droplets of same size. The final surface energy is
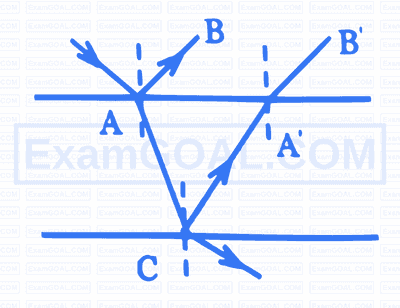
A ray of light of intensity ' I ' is incident on a parallel glass slab at a point ' $A$ ' as shown in figure. It undergoes partial reflection and refraction. At each reflection $25 \%$ of incident energy is reflected. The rays $A B$ and $A B$ undergo interference. The ratio $\frac{\mathrm{I}_{\text {max }}}{\mathrm{I}_{\text {min }}}$ is