
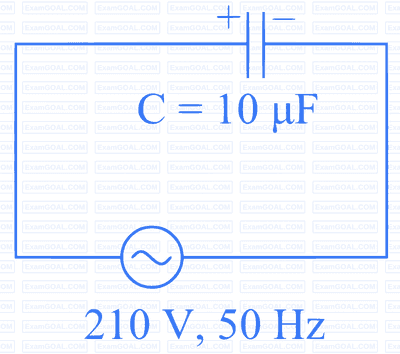
A $$10 \mu \mathrm{F}$$ capacitor is connected to a $$210 \mathrm{~V}, 50 \mathrm{~Hz}$$ source as shown in figure. The peak current in the circuit is nearly $$(\pi=3.14)$$ :

A metallic bar of Young's modulus, $$0.5 \times 10^{11} \mathrm{~N} \mathrm{~m}^{-2}$$ and coefficient of linear thermal expansion $$10^{-5}{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}^{-1}$$, length $$1 \mathrm{~m}$$ and area of cross-section $$10^{-3} \mathrm{~m}^2$$ is heated from $$0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ to $$100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ without expansion or bending. The compressive force developed in it is :

An iron bar of length $$L$$ has magnetic moment $$M$$. It is bent at the middle of its length such that the two arms make an angle $$60^{\circ}$$ with each other. The magnetic moment of this new magnet is :

If the plates of a parallel plate capacitor connected to a battery are moved close to each other, then
A. the charge stored in it, increases.
B. the energy stored in it, decreases.
C. its capacitance increases.
D. the ratio of charge to its potential remains the same.
E. the product of charge and voltage increases.
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below: