1
GATE CSE 1996
Subjective
+5
-0
A computer system has a three level memory hierarchy, with access time and hit ratios as shown below:

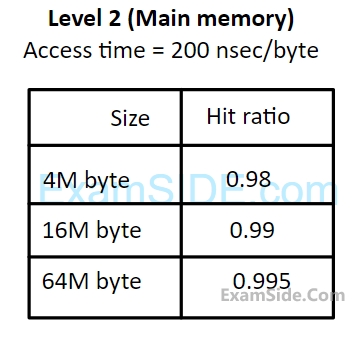




(i) What should be the minimum size of level $$1$$ and $$2$$ memories to achieve an average access time of less than $$100$$ nsec?
(ii) What is the average access time achieved using the chosen sizes of level $$1$$ and level $$2$$ memories?
2
GATE CSE 1996
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
It gives non-uniform priority to various devices.
3
GATE CSE 1996
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Both’s algorithm for integer multiplication gives worst performance when the multiplier pattern is
4
GATE CSE 1996
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Consider the following floating point number representation
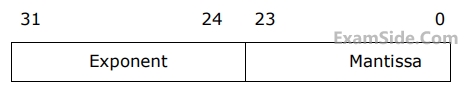

The exponent is in $$2’s$$ complement representation and mantissa is in the sign magnitude representation. The range of the magnitude of the normalized mantissa in this representation is
Paper analysis
Total Questions
Algorithms
6
Compiler Design
1
Computer Organization
5
Data Structures
6
Database Management System
1
Digital Logic
5
Discrete Mathematics
15
Operating Systems
11
Programming Languages
1
Theory of Computation
5
More papers of GATE CSE
GATE CSE 2025 Set 2
GATE CSE 2025 Set 1
GATE CSE 2024 Set 2
GATE CSE 2024 Set 1
GATE CSE 2023
GATE CSE 2022
GATE CSE 2021 Set 2
GATE CSE 2021 Set 1
GATE CSE 2020
GATE CSE 2019
GATE CSE 2018
GATE CSE 2017 Set 1
GATE CSE 2017 Set 2
GATE CSE 2016 Set 1
GATE CSE 2016 Set 2
GATE CSE 2015 Set 3
GATE CSE 2015 Set 1
GATE CSE 2015 Set 2
GATE CSE 2014 Set 3
GATE CSE 2014 Set 1
GATE CSE 2014 Set 2
GATE CSE 2013
GATE CSE 2012
GATE CSE 2011
GATE CSE 2010
GATE CSE 2009
GATE CSE 2008
GATE CSE 2007
GATE CSE 2006
GATE CSE 2005
GATE CSE 2004
GATE CSE 2003
GATE CSE 2002
GATE CSE 2001
GATE CSE 2000
GATE CSE 1999
GATE CSE 1998
GATE CSE 1997
GATE CSE 1996
GATE CSE 1995
GATE CSE 1994
GATE CSE 1993
GATE CSE 1992
GATE CSE 1991
GATE CSE 1990
GATE CSE 1989
GATE CSE 1988
GATE CSE 1987
GATE CSE
Papers
2023
2022
2020
2019
2018
2013
2012
2011
2010
2009
2008
2007
2006
2005
2004
2003
2002
2001
2000
1999
1998
1997
1996
1995
1994
1993
1992
1991
1990
1989
1988
1987