1
GATE CSE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A computer system has an $$L1$$ cache, an $$L2$$ cache, and a main memory unit connected as shown below. The block size in $$L1$$ cache is $$4$$ words. The block size in $$L2$$ cache is $$16$$ words. The memory access times are $$2$$ nanoseconds, $$20$$ nanoseconds and $$200$$ nanoseconds for $$L1$$ cache, $$L2$$ cache and main memory unit respectively.
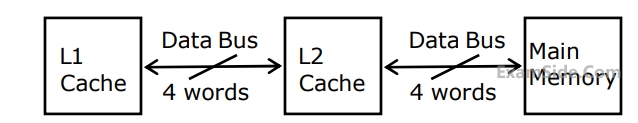

When there is a miss in $$L1$$ cache and a hit in $$L2$$ cache, a block is transferred from $$L2$$ cache to $$L1$$ cache. What is the time taken for this transfer?
2
GATE CSE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A $$5$$-stage pipelined processor has Instruction Fetch $$(IF),$$ Instruction Decode $$(ID),$$ Operand Fetch $$(OF),$$ Perform Operation $$(PO)$$ and Write Operand $$(WO)$$ stages. The $$IF, ID, OF$$ and $$WO$$ stages take $$1$$ clock cycle each for any instruction. The $$PO$$ stage takes $$1$$ clock cycle for $$ADD$$ and $$SUB$$ instructions, $$3$$ clock cycles for $$MUL$$ instruction, and $$6$$ clock cycles for $$DIV$$ instruction respectively. Operand forwarding is used in the pipeline. What is the number of clock cycles needed to execute the following sequence of instructions?
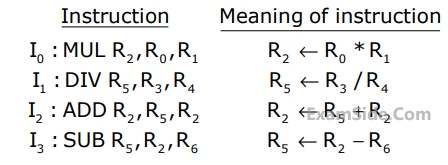

3
GATE CSE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A hash table of length 10 uses open addressing with hash function h(k)=k mod 10, and linear probing. After inserting 6 values into an empty hash table, the table is as shown below
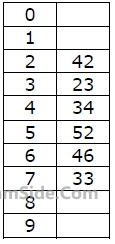 How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?
How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?
 How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?
How many different insertion sequences of the key values using the same hash function and linear probing will result in the hash table shown above?4
GATE CSE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The following C function takes a simply-linked list as input argument. It modifies the list by moving the last element to the front of the list and returns the modified list. Some part of the code is left blank.
typedef struct node {
int value;
struct node *next;
} Node;
Node *move_to_front(Node *head) {
Node *p, *q;
if ((head = = NULL: || (head->next = = NULL)) return head;
q = NULL; p = head;
while (p-> next !=NULL) {
q=P;
p=p->next;
}
return head;
} Paper analysis
Total Questions
Algorithms
3
Compiler Design
4
Computer Networks
5
Computer Organization
4
Data Structures
5
Database Management System
5
Digital Logic
4
Discrete Mathematics
10
Operating Systems
5
Programming Languages
2
Software Engineering
3
Theory of Computation
4
More papers of GATE CSE
GATE CSE 2025 Set 2
GATE CSE 2025 Set 1
GATE CSE 2024 Set 2
GATE CSE 2024 Set 1
GATE CSE 2023
GATE CSE 2022
GATE CSE 2021 Set 2
GATE CSE 2021 Set 1
GATE CSE 2020
GATE CSE 2019
GATE CSE 2018
GATE CSE 2017 Set 1
GATE CSE 2017 Set 2
GATE CSE 2016 Set 1
GATE CSE 2016 Set 2
GATE CSE 2015 Set 3
GATE CSE 2015 Set 1
GATE CSE 2015 Set 2
GATE CSE 2014 Set 3
GATE CSE 2014 Set 1
GATE CSE 2014 Set 2
GATE CSE 2013
GATE CSE 2012
GATE CSE 2011
GATE CSE 2010
GATE CSE 2009
GATE CSE 2008
GATE CSE 2007
GATE CSE 2006
GATE CSE 2005
GATE CSE 2004
GATE CSE 2003
GATE CSE 2002
GATE CSE 2001
GATE CSE 2000
GATE CSE 1999
GATE CSE 1998
GATE CSE 1997
GATE CSE 1996
GATE CSE 1995
GATE CSE 1994
GATE CSE 1993
GATE CSE 1992
GATE CSE 1991
GATE CSE 1990
GATE CSE 1989
GATE CSE 1988
GATE CSE 1987
GATE CSE
Papers
2023
2022
2020
2019
2018
2013
2012
2011
2010
2009
2008
2007
2006
2005
2004
2003
2002
2001
2000
1999
1998
1997
1996
1995
1994
1993
1992
1991
1990
1989
1988
1987