Heat and Thermodynamics · Physics · COMEDK
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
The total number of degrees of freedom associated with $2 \mathrm{~cm}^3$ of Nitrogen gas at normal temperature and pressure is:
[Given Avogadro number as ' N ' ]
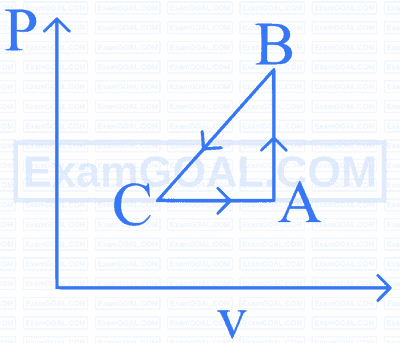
A sample of an ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure below. It absorbs 60 J of heat during the part AB and rejects 80 J of heat during CA . There is no heat exchanged during the process $\mathrm{BC} . \mathrm{A}$ work of 40 J is done on the gas during the part BC . If the internal energy of the gas at A is 1450 J , then the work done by the gas during the part CA is:
The coefficient of volume expansion of glycerine is $$49 \times 10^{-5} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}$$. The percentage change in its density for a $$50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ rise in temperature is
The latent heat of vaporisation of water is $$2240 \mathrm{~J}$$. If the work done in the process of vaporisation of $$1 \mathrm{~g}$$ is $$168 \mathrm{~J}$$, the increase in internal energy is
Internal energy of $$\mathrm{n}_1$$ moles of hydrogen at temperature T is equal to internal energy of $$\mathrm{m}_2$$ moles of helium at temperature 2T. The ratio $$\frac{n_1}{n_2}$$ is
A cylinder of fixed capacity 44.81 contains hydrogen gas at STP. What is the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of the gas in the cylinder by $$20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ ? ($$R=8.31 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}$$)
An iron piece of mass $$200 \mathrm{~g}$$ is kept inside a furnace for some time and then put in a calorimeter of water equivalent $$20 \mathrm{~g}$$ containing $$230 \mathrm{~g}$$ of water at $$20 \mathrm{C}$$. The steady state temperature attained by the mixture is $$60^{\circ}$$. The temperature of the furnace is (Specific heat capacity of iron is $$470 \mathrm{~J~kg}^{-1} \mathrm{C}^{-1}$$ )
An ideal gas changes its state from $$\mathrm{A}$$ to $$\mathrm{C}$$ in two different paths $$\mathrm{ABC}$$ and $$\mathrm{AC}$$. The internal energy of the gas at state $$\mathrm{C}$$ is $$20 \mathrm{~J}$$ and at state $$\mathrm{B}$$ is $$10 \mathrm{~J}$$. Heat supplied to the gas to go from $$\mathrm{B} \rightarrow \mathrm{C}$$ is

If pressure of an ideal gas is increased by keeping temperature constant the kinetic energy will
A cubical box of side $$2 \mathrm{~m}$$ contains helium gas. It was observed that in a time of 1 second, an atom travelling with the root-mean-square speed parallel to one of the edges of the cube, made 250 hits with one of the walls, without any collision with other atoms. The average kinetic energy of the helium gas is Take $$R=\frac{25}{3} \mathrm{~J} / \mathrm{mol}-\mathrm{K}$$ and $$\mathrm{kB}=1.38 \times 10^{-23} \mathrm{JK}{ }^{-1}$$
A glass of hot water cools from $$90^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ to $$70^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ in 3 minutes when the temperature of surroundings is $$20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. What is the time taken by the glass of hot water to cool from $$60^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ to $$40^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ if the surrounding temperature remains the same at $$20^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ ?
A cubical box of side $$1 \mathrm{~m}$$ contains Boron gas at a pressure of $$100 \mathrm{~Nm}^{-2}$$. During an observation time of 1 second, an atom travelling with the rms speed parallel to one of the edges of the cube, was found to make 500 hits with a particular wall, without any collision with other atoms. The total mass of gas in the box in gram is
A one $\mathrm{kg}$ block of ice at $$-1.5^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ falls from a height of $$1.5 \mathrm{~km}$$ and is found melting. The amount of ice melted due to fall, if $$60 \%$$ energy is converted into heat is (Specific heat capacity of ice is $$0.5 \mathrm{~cal} \mathrm{~g}^{-1} \mathrm{~C}^{-1}$$, Latent heat of fusion of ice $$=80 \mathrm{~cal~g}^{-1}$$ )
An electric bulb of volume $$300 \mathrm{~cm}^3$$ was sealed off during manufacture at a pressure of $$1 \mathrm{~mm}$$ of mercury at $$27{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. The number of air molecules contained in the bulb is, $$(\mathrm{R}=8.31 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}$$ and $$N_A=6.02 \times 10^{23})$$
The mean energy per molecule for a diatomic gas is
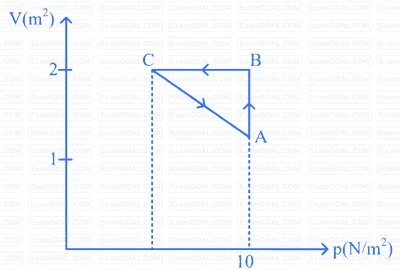
A gas is taken through the cycle $$A \rightarrow B \rightarrow C \rightarrow A$$, as shown in figure. What is the net work done by the gas?

The gases carbon monoxide $$(\mathrm{CO})$$ and nitrogen at the same temperature have kinetic energies $$E_1$$ and $$E_2$$, respectively. Then,
An ideal gas goes from state $$A$$ to state $$B$$ via three different processes as indicated in the $$p$$-$$V$$ diagram. If $$Q_1, Q_2$$ and $$Q_3$$ indicate the heat absorbed by the three processes and $$\Delta U_1, \Delta U_2$$ and $$\Delta U_3$$ indicate the change in internal energy along the three processes respectively, then

If $$150 \mathrm{~J}$$ of heat is added to a system and the work done by the system is $$110 \mathrm{~J}$$, then change in internal energy will be
Two slabs are of the thicknesses $$d_1$$ and $$d_2$$. Their thermal conductivities are $$K_1$$ and $$K_2$$, respectively. They are in series. The free ends of the combination of these two slabs are kept at temperatures $$\theta_1$$ and $$\theta_2$$. Assume $$\theta_1 > \theta_2$$. The temperature $$\theta$$ of their common junction is
A cylinder of radius $$r$$ and of thermal conductivity $$K_1$$ is surrounded by a cylindrical shell of inner radius $$r$$ and outer radius $$2 r$$ made of a material of thermal conductivity $$K_2$$. The effective thermal conductivity of the system is
In an adiabatic expansion of air, the volume is increased by $$6.2 \%$$. The percentage change in pressure is $$(\gamma=1.4)$$
If the ratio of specific heat of a gas at constant pressure to that at constant volume is $$\gamma$$, the change in internal energy of a mass of a gas when the volume changes from $$\mathrm{V}$$ to $$3 \mathrm{~V}$$ at constant pressure is
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speed of $$120 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$$ at $$88^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ and 1 atmospheric pressure. The root mean square speed of the molecules at $$127^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ and 2 atmospheric pressure is
Two black bodies $$\mathrm{P}$$ and $$\mathrm{Q}$$ have equal surface areas and are kept at temperatures $$127^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ and $$27^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ respectively. The ratio of thermal power radiated by A to that by B is
If heat engine is filled at temperature 27$$^\circ$$C and heat of 100 k cal is taken from source at temperature 677$$^\circ$$C. Work done (in J) is
From the following p-V diagram, an ideal gas undergoing a change of state from A to B. Four different processes I, II, III and IV as shown in the figure may lead to same change of state.

An ideal gas is taken through the cycle A $$\to$$ B $$\to$$ C $$\to$$ A, as shown in the figure. If the net heat supplied to the gas in the cycle is 5 J, the work done by the gas in the process C $$\to$$ A is,
The average kinetic energy of a molecule in air at room temperature of 20$$^\circ$$C
There are two identical containers C$$_1$$ and C$$_2$$ containing to identical gases. Gas in C$$_1$$ is reduced to half of its original volume adiabatically, while the gas in container C$$_2$$ is also reduced to half of its initial volume isothermally. Find the ratio of final pressure in these containers. ($$\gamma$$ be the adiabatic constant).
In which mode of transmission, the heat waves travel along straight line with the speed of light?
Consider a compound slab consisting of two different materials having equal lengths, thickness and thermal conductivities K and 2K respectively. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the slab is
In an adiabatic process with the ratio of two specific heat, $$\gamma=\frac{3}{2}$$, pressure is increased by $$\frac{2}{3}$$%, then decrease in the volume will be
For an ideal gas, coefficient of volume expansion is given by
Which of the following is not a green house gas?
The collision of the molecules of an ideal gas is taken as
The average energy associated with a monoatomic molecule is
Carnot cycle of an engine is given below

Total work done by the gas in one cycle is
A compound slab is made of two parallel plates of copper and brass of the same thickness and having thermal conductivities in the ratio 4 : 1. The free face of copper is at 0$$^\circ$$C. The temperature of the interface is 20$$^\circ$$C. What is the temperature of the free face of brass?
In mm$$^3$$ of a gas is compressed at 1 atmospheric pressure and temperature 27$$^\circ$$C to 627$$^\circ$$C. What is the final pressure under adiabatic condition?
($$\gamma$$ for the gas = 1.5)
If sink is at a temperature of $$-39\Upsilon$$C and source at 0$$^\circ$$C, then efficiency will be
Equal volumes of two gases, having their densities in the ratio of 1 : 16 exert equal pressures on the walls of two containers. The ratio of their rms velocities $$\left(\frac{c_1}{c_2}\right)$$
A gaseous mixture consists of 16 g of helium and 16 g of oxygen. The ratio $$C_p/C_V$$ of the mixture is