For a given mass of a gas at constant temperature, the volume and the pressure are $V$ and $p$ respectively. Then the slope of the graph drawn between $\log _e V$ on $X$-axis and $\log _e p$ on $Y$-axis is
An ideal gas at $127^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ is compressed suddenly to $8 / 27 \mathrm{}$of its initial volume. If $\gamma=5 / 3$ for an ideal gas, then rise in its temperature is
An insulating cylinder contains 4 moles of an ideal diatomic gas. When a heat $Q$ is supplied to it, 2 moles of the gas molecules dissociate. If the temperature of the gas remains constant, then the value of $Q$ is ( $R=$ universal gas constant)
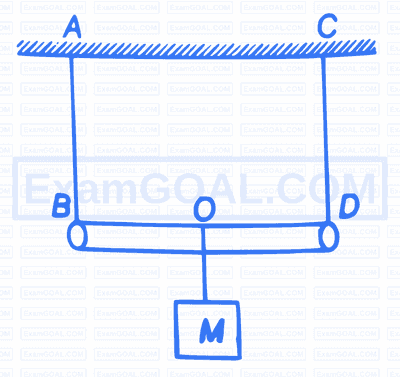
A rod of length $L$ and negligible mass is suspended by two identical strings $A B$ and $C D$ as shown in the figure A mass $M$ is suspended from point $O$ which is at a distance $x$ from $B$. If the frequency of the first harmonic of $A B$ is equal to the frequency of the second harmonic of $C D$, then the value of $x$ is