If a source emitting waves of frequency ' $F$ ' moves towards an observer with a velocity $\frac{\mathrm{V}}{3}$ and the observer moves away from the source with a velocity $\frac{\mathrm{V}}{4}$, the apparent frequency as heard by the observer will be ( $\mathrm{V}=$ velocity of sound)
In hydrogen atom, transition from the state $\mathrm{n}=6$ to $n=1$ results in ultraviolet radiation. Infrared radiation will be obtained in the transition
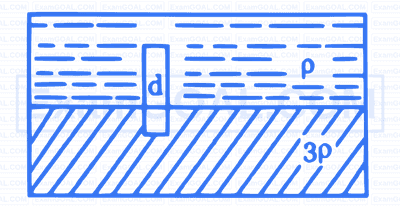
A solid cylinder of length $l$ and cross-sectional area $\frac{a}{5}$ is immersed such that it floats with its axis vertical at the liquid-liquid interface with length $l / 4$ in the denser liquid as shown in figure. The lower density liquid ( $\rho$ ) is open to atmosphere having pressure $\mathrm{P}_0$. The density d of solid cylinder is
Two capacitors of $100 \mu \mathrm{~F}$ and $50 \mu \mathrm{~F}$ are connected in parallel. If the potential difference across $100 \mu \mathrm{~F}$ is 20 V and across $50 \mu \mathrm{~F}$ is 40 V , then the common potential of the parallel combination will be (same polarities of the capacitor connected together)