If $$A=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}1 & 0 & 2 \\ -1 & 1 & -2 \\ 0 & 2 & 1\end{array}\right], \operatorname{adj} A=\left[\begin{array}{ccc}5 & x & -2 \\ 1 & 1 & 0 \\ -2 & -2 & y\end{array}\right]$$, then value of $$x+y$$ is
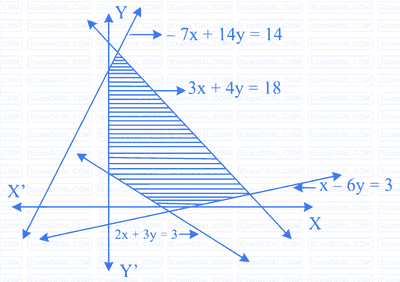
The shaded figure given below is the solution set for the linear inequations. Choose the correct option.
$$\begin{aligned} & \text { If the function } \mathrm{f}(\mathrm{x})=1+\sin \frac{\pi}{2}, \quad-\infty<\mathrm{x} \leq 1 \\ & =\mathrm{ax}+\mathrm{b}, \quad 1<\mathrm{x}<3 \\ & =6 \tan \frac{x \pi}{12}, \quad 3 \leq x<6 \\ \end{aligned}$$
is continuous in $$(-\infty, 6)$$, then the values of $$\mathrm{a}$$ and $$\mathrm{b}$$ are respectively.
If $$\int \frac{x^3}{\sqrt{1+x^2}} d x=a\left(1+x^2\right)^{\frac{3}{2}}+b \sqrt{1+x^2}+c$$, then $$a+b=$$, (where $$c$$ is constant of integration)