GATE PI 2008
GATE PI
1
In hollow cylindrical parts made by centrifugal casting, the density of the part is
2
In sand casting of hallow part of lead, a cylindrical core of diameter $$120mm$$ and height $$180mm$$ is placed inside the mould cavity. The densities of core material and lead are $$1600kg/{m^3}$$ and $$11300kg/{m^3}$$ respectively. The net force (in $$N$$) that tends to lift the core during pouring of molten metal will be
3
The inverse of matrix $$\left[ {\matrix{
0 & 1 & 0 \cr
1 & 0 & 0 \cr
0 & 0 & 1 \cr
} } \right]$$ is
4
The value of the integral $$\,\,\int\limits_{ - \pi /2}^{\pi /2} {\left( {x\,\cos \,x} \right)dx\,\,} $$ is
5
The value of the expansion $$\mathop {Lim}\limits_{x \to 0} \left[ {{{\sin \left( x \right)} \over {{e^x}X}}} \right]\,\,$$ is
6
If $$\overrightarrow r $$ is the position vector of any point on a closed surface $$S$$ that encloses the volume $$V$$ then $$\,\,\int {\int\limits_s {\left( {\overrightarrow r \,.\,d\overrightarrow s } \right)\,\,} } $$ is equal to
7
In a game, two players $$X$$ and $$Y$$ toss a coin alternately. Whoever gets a 'head' first, wins the game and the game is terminated. Assuming that players $$X$$ starts the game the probability of player $$X$$ winning the game is
8
For a random variable $$\,x\left( { - \infty < x < \infty } \right)\,\,$$ following normal distribution, the mean is $$\,\mu = 100\,\,.$$ If the probability is $$\,\,P = \alpha \,\,$$ for $$\,\,x \ge 110.\,\,\,$$ Then the probability of $$x$$ lying $$b/w$$ $$90$$ and $$110$$ i.e., $$\,P\left( {90 \le x \le 110} \right)\,\,$$ and equal to
9
The solutions of the differential equation $${{{d^2}y} \over {d{x^2}}} + 2{{dy} \over {dx}} + 2y = 0\,\,$$ are
10
The value of the expression $${{ - 5 + 10i} \over {3 + 4i}}$$ is
11
The eigen vector pair of the matrix $$\left[ {\matrix{
3 & 4 \cr
4 & { - 3} \cr
} } \right]$$ is
12
Laplace transform of $$8$$ $${t^3}$$ is
13
Laplace transform of $$sin$$ $$ht$$ is
14
Two pipes of uniform section but different diameters carry water at the same volumetric flow rate. Water properties are the same in the two pipes. The Reynolds number, based on the pipe diameter,
15
Oil is being pumped through a straight pipe, the pipe length, diameter and volumetric flow rate are all doubled in a new arrangement. The pipe friction factor, however, remains constant. The ratio of pipe frictional losses in the new arrangement to that in the original configuration would be
16
Two pipes of inner diameter $$100mm$$ and outer diameter $$110mm$$ each are joined by flash butt welding using $$30V$$ power supply. At the interface, $$1mm$$ of material melts from each pipe which has a resistance of $$42$$ Ohms.If the unit melt energy is $$64.4$$ $$MJ/{m^3}$$, then time required for welding (in $$S$$) is
17
Aluminium strips of $$2mm$$ thickness are joined together by resistance spot welding process by applying an electric current $$6000$$$$A$$ for $$0.15sec$$. The heat required for melting aluminium is $$2.9J/m{m^3}.$$ The diameter and thickness of the weld nugget are found to be $$5$$ $$mm$$ and $$2.5mm$$ respectively. Assuming the electrical resistance to be $$75$$ micro-ohms, the percentage of total energy utilized in forming the weld nugget is
18
Which of the following powders should be fed for effective oxy-fuel cutting of stainless steel
19
Which pair among the following solid state welding processes uses heat from an external source
$$P$$- Diffusion welding
$$Q$$- Friction welding
$$R$$- Ultrasonic welding
$$S$$- Forge welding
$$P$$- Diffusion welding
$$Q$$- Friction welding
$$R$$- Ultrasonic welding
$$S$$- Forge welding
20
During machining, the wear land $$(h)$$ has been plotted against machining time $$(T)$$ as given in the following figure.
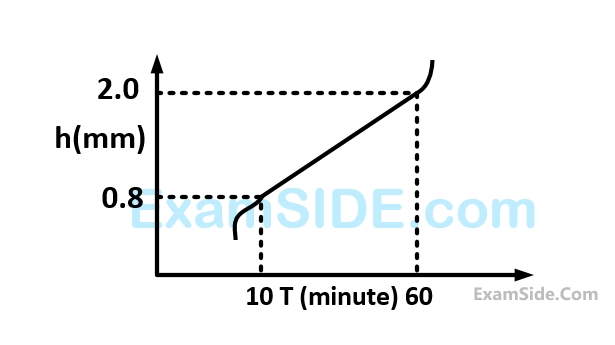

For a critical wear land of $$1.8mm,$$ the cutting tool life (in $$min$$) is
21
Diamond cutting tools are not recommended for machining of ferrous metals to
22
In an orthogonal cutting experiment, an $$HSS$$ tool having the following tool signature in the orthogonal reference system $$(ORS)$$ has been used: $$0-10-7-7-10-75-1$$
Given : Width of cut $$=3.6mm;$$
Shear strength of work piece material $$460N/m{m^2};$$
Depth of cut $$=0.25mm;$$
Coefficient of friction at chip tool interface $$=0.7.$$
Given : Width of cut $$=3.6mm;$$
Shear strength of work piece material $$460N/m{m^2};$$
Depth of cut $$=0.25mm;$$
Coefficient of friction at chip tool interface $$=0.7.$$
Shear plane angle (in degrees) for minimum cutting force is
23
In an orthogonal cutting experiment, an $$HSS$$ tool having the following tool signature in the orthogonal reference system $$(ORS)$$ has been used: $$0-10-7-7-10-75-1$$
Given : Width of cut $$=3.6mm;$$
Shear strength of work piece material $$460N/m{m^2};$$
Depth of cut $$=0.25mm;$$
Coefficient of friction at chip tool interface $$=0.7.$$
Given : Width of cut $$=3.6mm;$$
Shear strength of work piece material $$460N/m{m^2};$$
Depth of cut $$=0.25mm;$$
Coefficient of friction at chip tool interface $$=0.7.$$
Minimum Power requirement (in $$KW$$) at a cutting speed of $$150m/min$$ is
24
Brittle materials are machined with tools having zero or negative rake angles because it
25
The quick return mechanism used in shaper has rocker arm drive of length $$200mm.$$ If the crank radius is $$50mm$$ and the offset between crank center and rocker arm pivot is $$20mm,$$ length of the stroke (in meters) is
26
A stepper motor has $$150$$ steps. The output shaft of the motor is directly coupled to a lead screw of pitch $$4mm,$$ which drives a table. If the frequency of pulse supply to the motor is $$200Hz$$, the speed of the table (in $$mm/min)$$ is
27
Suppose point $$P1$$ in $$APT$$ (Automatically programmed Tool) programming is coded by statement
$$P1 = POINT/XSMALL,\,\,\,INTOF,\,\,\,LN1,\,\,CR1$$
$$P1 = POINT/XSMALL,\,\,\,INTOF,\,\,\,LN1,\,\,CR1$$
The coded geometric situation without causing error is
28
In a $$CNC$$ feed drive, a stepper motor with step angle of $$1.8deg$$ drives a lead screw with pitch of $$2mm.$$ The basic length unit $$(BLU)$$ for this drive is
29
A $$10mm$$ diameter annealed steel wire is drawn through a die at a speed of $$0.5/sec$$ to reduce the diameter by $$20\% $$. The yield stress of the material is $$800MPa.$$
Neglecting friction and strain hardening, the stress required for drawing (in $$MPa$$) is
30
Match the following


31
A blank of $$50$$ $$mm$$ diameter is to be sheared from a sheet of $$2.5$$ $$mm$$ thickness. The required radial clearance between the die and the punch is $$6\% $$ of sheet thickness. The punch and die diameter $$(mm)$$ for this blanking operation respectively are
32
In a rolling process, thickness of a strip is reduced from $$4mm$$ to $$3mm$$ using $$300mm$$ diameter rolls rotating at $$100rpm.$$ The velocity of the strip (in $$m/sec$$) at the neutral point is
33
A $$10mm$$ diameter annealed steel wire is drawn through a die at a speed of $$0.5/sec$$ to reduce the diameter by $$20\% $$. The yield stress of the material is $$800MPa.$$
The power required for the drawing process (in $$kW$$ ) is
34
By application of tensile force, the cross sectional area of bar $$' P '$$ is first reduced by $$30\% $$ and then by an additional $$20\% $$. Another bar $$'Q'$$ of the same material is reduced in cross sectional area by $$50\% $$ in a single step by applying tensile force. After deformation, the true strain in bar $$'P'$$ and bar $$'Q'$$ will, respectively, be
35
The following data are given for calculating limits of dimensions and tolerances for a hole: Tolerance unit $$'i'$$ (microns) $$=0.45$$ $${\left( D \right)^{1/3}} + 0.001D.$$ The unit of $$D$$ is $$mm.$$ Diameter step is $$18-30.$$ If the fundamental deviation for hole $$H$$ is zero and $${\rm I}T8 = 26i$$ the maximum and minimum limits of dimension for a $$25{H_8}$$ hole (in $$mm$$) are
36
An experimental setup is planned to determine the taper of work piece as shown in the figure. If the two precision rollers have radii $$8mm$$ and $$5mm$$ and the total thickness of slip gauges inserted between the rollers is $$15.54mm,$$ the taper angle $$'\theta '$$ is

