Motion · Physics · WB JEE
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
The distance travelled by an object along a straight line in time t is given by $$s = 3 - 4t + 5{t^2}$$, the initial velocity of the object is
Acceleration-time $(a-t)$ graph of a body is shown in the figurd. Corresponding velocity-time $(v-t)$ graph is

Ruma reached the metro station and found that the escalator was not working. She walked up the stationary escalator with velocity $v_1$ in time $t_1$. On other day if she remains stationary on the escalator moving with velocity $v_2$, then escalator takes her up in time $t_2$. The time taken by her to walk up with velocity $v_1$ on the moving escalator will be
The acceleration-time graph of a particle moving in a straight line is shown in the figure. If the initial velocity of the particle is zero then the velocity-time graph of the particle will be

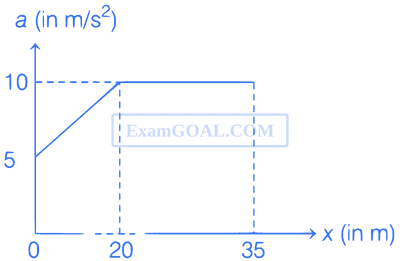
The acceleration versus distance graph for a particle moving with initial velocity 5 m/s is shown in the figure. The velocity of the particle at x = 35 m will be