Current Electricity · Physics · KCET
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
$$ \text { In the following circuit, the terminal voltage across the cell is } $$

Two cells of emfs $E_1$ and $E_2$ and internal resistances $r_1$ and $r_2\left(E_2>E_1\right.$ and $\left.r_2>r_1\right)$ respectively, are connected in parallel as shown in figure. The equivalent emf of the combination is $\mathrm{E}_{\text {eq. }}$. Then

The variations of resistivity $\rho$ with absolute temperature T for three different materials $\mathrm{X}, \mathrm{Y}$ and Z are shown in the graph below. Identify the materials $\mathrm{X}, \mathrm{Y}$ and Z .

Given, a current carrying wire of non-uniform cross-section, which of the following is constant throughout the length of wire?
The graph between variation of resistance of a metal wire as a function of its diameter keeping other parameters like length and temperature constant is
Two similar galvanometers are covered into an ammeter and a milliammeter. The shunt resistance of ammeter as compared to the shunt resistance of milliammeter will be
The range of electrical conductivity $(\sigma)$ and resistivity $(\rho)$ for metals, among the following, is
In an experiment to determine the figure of merit of a galvanometer by half deflection method, a student constructed the following circuit.

He unplugged a resistance of $5200 \Omega$ in R . When $\mathrm{K}_1$ is closed and $\mathrm{K}_2$ is open, the deflection observed in the galvanometer is 26 div. When $K_2$ is also closed and a resistance of $90 \Omega$ is removed in S , the deflection between 13 div. The resistance of galvanometer is nearly
E is the electric field inside a conductor whose material has conductivity $\sigma$ and resistivity $\rho$. The current density inside the conductor is $\mathbf{J}$. The correct form of Ohm's law is
In the circuit shown, the end $A$ is at potential $V_0$ and end $B$ is grounded. The electric current $I$ indicated in the circuit is

The electric current flowing through a given conductor varies with time as shown in the graph below. The number of free electrons which flow through a given cross-section of the conductor in the time interval $0 \leq t \leq 20 \mathrm{~s}$ is

The $I-V$ graph for a conductor at two different temperatures $100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ and $400^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ is as shown in the figure. The temperature coefficient of resistance of the conductor is about (in per degree Celsius)

An electric blub of $60 \mathrm{~W}, 120 \mathrm{~V}$ is to be connected to 220 V source. What resistance should be connected in series with the bulb, so that the bulb glows properly?
In an experiment to determine the temperature coefficient of resistance of a conductor, a coil of wire $X$ is immersed in a liquid. It is heated by an external agent. A meter bridge set up is used to determine resistance of the coil $X$ at different temperatures. The balancing points measured at temperatures $t_1=0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ and $t_2=100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ are 50 cm and 60 cm respectively. If the standard resistance taken out is $S=4 \Omega$ in both trials, the temperature coefficient of the coil is

A wire of resistance $$R$$ is connected across a cell of emf $$(\varepsilon)$$ and internal resistance $$(r)$$. The current through the circuit is $$I$$. In time $$t$$, the work done by the battery to establish the current $$I$$ is
For a given electric current the drift velocity of conduction electrons in a copper wire is $$v_d$$ and their mobility is $$\mu$$. When the current is increased at constant temperature
Ten identical cells each emf $$2 \mathrm{~V}$$ and internal resistance $$1 ~\Omega$$ are connected in series with two cells wrongly connected. A resistor of $$10 ~\Omega$$ is connected to the combination. What is the current through the resistor?
The equivalent resistance between the points A and B in the following circuit is

The resistance of a carbon resistor is $$4.7 ~\mathrm{k} \Omega \pm 5 \%$$. The colour of the third band is
The four bands of a colour coded resistor are of the colours grey, red, gold and gold. The value of the resistance of the resistor is
A moving coil galvanometer is converted into an ammeter of range 0 to $$5 \mathrm{~mA}$$. The galvanometer resistance is $$90 \Omega$$ and the shunt resistance has a value of $$10 \Omega$$. If there are 50 divisions in the galvanometer-turned-ammeter on either sides of zero, its current sensitivity is
A charged particle is moving in an electric field of $$3 \times 10^{-10} \mathrm{Vm}^{-1}$$ with mobility $$2.5 \times 10^6 \mathrm{~m}^2 / \mathrm{V}-\mathrm{s}$$, its drift velocity is
Wire bound resistors are made by winding the wires of an alloy of
10 identical cells each potential $$E$$ and internal resistance $$r$$ are connected in series to form a closed circuit.
Determine the potential difference across three cells using an ideal voltmeter.
In an atom electrons revolve around the nucleus along a path of radius $$0.72\mathop A\limits^o$$ making $$9.4 \times 10^{18}$$ revolutions per second. The equivalent currents is [given, $$e=1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}$$]
When a metal conductor connected to left gap of a meter bridge is heated, the balancing point
A wire of a certain material is stretched slowly by $$10 \%$$. Its new resistance and specific resistance becomes respectively
A galvanometer of resistance $$50 \Omega$$ is connected to a battery $$3 \mathrm{~V}$$ along with a resistance $$2950 \Omega$$ in series. A full scale deflection of 30 divisions is obtained in the galvanometer. In order to reduce this deflection to 20 divisions, the resistance in series should be
If voltage across a bulb rated $$220 \mathrm{~V}, 100 \mathrm{~W}$$ drops by $$2.5 \%$$ of its rated value, then the percentage of the rated value by which the power would decrease is
A wire of resistance $$3 \Omega$$ is stretched to twice its original length. The resistance of the new wire will be
In the given arrangement of experiment on meter bridge, if $$A D$$ corresponding to null deflection of the galvanometer is $$X$$, what would be its value if the radius of the wire $$A B$$ is doubled?

A copper wire of length $$1 \mathrm{~m}$$ and uniform cross-sectional area $$5 \times 10^{-7} \mathrm{~m}^2$$ carries a current of $$1 \mathrm{~A}$$. Assuming that, there are $$8 \times 10^{28}$$ free electrons per $$\mathrm{m}^3$$ in copper, how long will an electron take to drift from one end of the wire to the other?
Consider an electrical conductor connected across a potential difference $$V$$. Let $$\Delta q$$ be a small charge moving through it in time $$\Delta t$$. If $$I$$ is the electric current through it,
I. the kinetic energy of the charge increases by $$I V \Delta t$$.
II. the electric potential energy of the charge decreases by $$I V \Delta t$$.
III. the thermal energy of the conductor increases by $$I V \Delta t$$.
Choose the correct option.
A metal rod of length $$10 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and a rectangular cross-section of $$1 \mathrm{~cm} \times \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~cm}$$ is connected to a battery across opposite faces. The resistance will be
A car has a fresh storage battery of emf $$12 \mathrm{~V}$$ and internal resistance $$2 \times 10^{-2} \Omega$$. If the starter motor draws a current of $$80 \mathrm{~A}$$. Then, the terminal voltage when the starter is On is
A potentiometer has a uniform wire of length $$5 \mathrm{~m}$$. A battery of emf $$10 \mathrm{~V}$$ and negligible internal resistance is connected between its ends. A secondary cell connected to the circuit gives balancing length at $$200 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The emf of the secondary cell is
The colour code for a carbon resistor of resistance $$0.2 \mathrm{k} \Omega \pm 10 \%$$ is
Each resistance in the given cubical network has resistance of $$1 \Omega$$ and equivalent resistance between $$A$$ and $$B$$ is

$$I-V$$ characteristic of a copper wire of length $$L$$ and area of cross-section $$A$$ is shown in figure. The slope of the curve becomes

The readings of ammeter and voltmeter in the following circuit are respectively

Though the electron drift velocity is small and electron charge is very small, a conductor can carry an appreciably large current because
Masses of three wires of copper are in the ratio $$1: 3: 5$$ and their lengths are in the ratio $$5: 3: 1$$. The ratio of their electrical resistance are
In the given circuit, the current through 2$$\Omega$$ resistor is

Kirchhoff 's junction rule is a reflection of
The variation of terminal potential difference $$V$$ with current flowing through a cell is as shown. The emf and internal resistance of the cell are

In a potentiometer experiment, the balancing point with a cell is at a length $$240 \mathrm{~cm}$$. On shunting the cell with a resistance of $$2 \Omega$$, the balancing length becomes $$120 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The internal resistance of the cell is



Of the following graphs, the one that correctly represents the $I-V$ characteristics of a 'Ohmic device' is
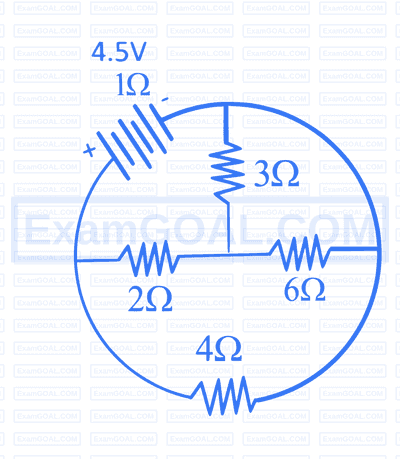
$$ \text { The value of } I \text { in the figure shown below is } $$
