Chemistry
By passing electric current, $\mathrm{NaClO}_3$ is converted in to $\mathrm{NaClO}_4$ according to the following equation
$$ \mathrm{NaClO}_3+\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O} \longrightarrow \mathrm{NaClO}_4+\mathrm{H}_2 $$
How many moles of $\mathrm{NaClO}_4$ will be formed when three Faradays of charges is passed through $\mathrm{NaClO}_3$ ?

The standard reduction potential at 298 K for the following half cell reaction
$$ \begin{aligned} & 2 \mathrm{n}^{2+}(a q)+2 e^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Zn}(s) ; E^0=-0.762 \mathrm{~V} \\ & \mathrm{Cr}^{3+}(a q)+3 e^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Cr}(s) ; E^0=0.740 \mathrm{~V} \\ & 2 \mathrm{H}^{+}(a q)+2 e^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Hz}(g) ; E^0=0.0 \mathrm{~V} \\ & \mathrm{~F}_2(g)+2 e^{-} \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{~F}^{-}(a q) ; E^0=2.87 \mathrm{~V} \end{aligned} $$
Which of the following is strongest reducing agent?
Which of the following is correct electron dot structure of $\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}$ molecule?
In the following sequence of reactions
$$ \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{Br} \xrightarrow{\mathrm{KCN}} A \xrightarrow{\mathrm{H}_3 \mathrm{O}^{-}} B \xrightarrow{\mathrm{LiAl} / \mathrm{H}_4} $$
The end product $C$ is
In the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride solution, which of the half cell reaction will occur at anode?
Mathematics
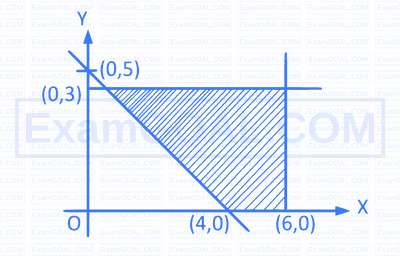
$$ \int\limits_{-\pi / 2}^{\pi / 2} \frac{d x}{e^{\sin x}+1} $$
$$ \int\limits_0^{\pi / 2} \frac{1}{a^2 \cdot \sin ^2 x+b^2 \cdot \cos ^2 x} d x $$
$$ \int \sqrt{x^2+2 x+5} d x \text { is equal to } $$
$$ \text { If } y=\left|\begin{array}{ccc} f(x) & g(x) & h(x) \\ l & m & n \\ a & b & c \end{array}\right| \text {, then } \frac{d y}{d x} \text { is equal to } $$
General solution of differential equations
$\frac{d y}{d x}+y=1(y \neq 1)$ is
If $A=\frac{1}{\pi}\left|\begin{array}{ll}\sin ^{-1}(\pi x) & \tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{\pi}\right) \\ \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{\pi}\right) & \cot ^{-1}(\pi x)\end{array}\right|$
$B=\left|\begin{array}{cc}-\cos ^{-1}(\pi x) & \tan ^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{\pi}\right) \\ \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{x}{\pi}\right) & -\tan ^{-1}(\pi x)\end{array}\right|$,
then $A-B$ is :
The probability distribution of $X$ is
$$ \begin{array}{|c|l|c|c|c|} \hline \boldsymbol{X} & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 \\ \hline \boldsymbol{P}(\boldsymbol{X}) & 0.3 & k & 2 k & 2 k \\ \hline \end{array} $$
$$ \text { The value of } k \text { is } $$$$The\,\,value\,\,of\,\,\mathop {\lim }\limits_{\theta \to 0} {{1 - \cos 4\theta } \over {1 - \cos 6\theta }}\,\,is$$
The integrating factor of the differential equation
$x \cdot \frac{d y}{d x}+2 y=x^2$ is $(x \neq 0)$
Physics
Of the following graphs, the one that correctly represents the $I-V$ characteristics of a 'Ohmic device' is

A bar magnet is allowed to fall vertically through a copper coil placed in a horizontal plane. The magnet falls with a net acceleration, is

In the A.C. circuit shown, keeping ' $K$ ' pressed, if an iron rod inserted into the coil, the bulb in the circuit,

In the figure shown, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.2 V , the voltage difference between $A$ and $B$ is

A straight wire of length 50 cm carrying a current of 2.5 A is suspended in mid-air by a uniform magnetic field of 0.5 T (as shown in figure). The mass of the wire is ( $g=10 \mathrm{~ms}^{-2}$ )

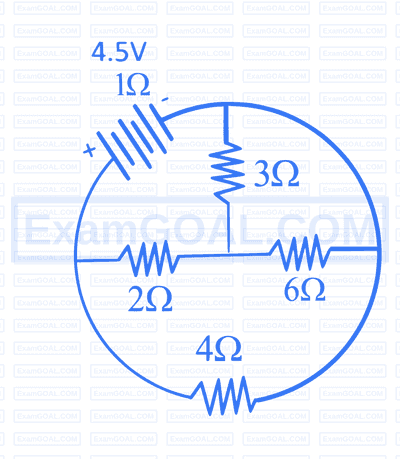
$$ \text { The value of } I \text { in the figure shown below is } $$
